常州做的网站的公司推广网站源码
一、@interface 关键字
我们想定义一个自己的注解 需要使用 @interface 关键字来定义。
如定义一个叫 MyAnnotation 的注解:
public @interface MyAnnotation { }二、元注解
光加上 @interface 关键字 还不够,我们还需要了解5大元注解
@Retention@Target@Documented@Inherited(JDK8 引入)@Repeatable(JDK8 引入)
1) @Retention 指定注解的生命周期
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)其中Retention是一个枚举类:
- RetentionPolicy.SOURCE : 注解只保留在源文件,当Java文件编译成class文件的时候,注解被遗弃(.java文件)
- RetentionPolicy.CLASS :注解被保留到class文件,但jvm加载class文件时候被遗弃,这是默认的生命周期(.class文件)
- RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME: 注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在(内存中的字节码)
2) @Target指定注解可以修饰的元素类型
@Target(ElementType.Field)- ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE - 标记的注解可以应用于注解类型。
- ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR - 标记的注解可以应用于构造函数。
- ElementType.FIELD - 标记的注解可以应用于字段或属性。
- ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE - 标记的注解可以应用于局部变量。
- ElementType.METHOD - 标记的注解可以应用于方法。
- ElementType.PACKAGE - 标记的注解可以应用于包声明。
- ElementType.PARAMETER - 标记的注解可以应用于方法的参数。
- ElementType.TYPE - 标记的注解可以应用于类的任何元素。
3)@Documented
指定注解会被JavaDoc工具提取成文档。默认情况下,JavaDoc是不包括文档的
4)@Inherited
表示该注解会被子类继承,注意,仅针对类,成员属性、方法并不受此注释的影响。
5)@Repeatable
表示注解可以重复使用,为了解决同一个注解不能重复在同一类/方法/属性上使用的问题。
其中最常用的就是 @Retention 跟 @Target。
三、简单实现
例如实现一个简单,在标记注解的地方打印一句日志。
定义一个 MyAnnotation 注解,并且定义一个属性 message 默认值是 ”aaa“。先将该注解加到字段上,看能不能获取到。
//注解用于字段上
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
//运行时使用
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {String message() default "aaa";}定义一个Student类用于测试:
@Data
public class Student {@JSONField(ordinal =0)@MyAnnotation(message = "AAAAAAAAA")public String name;@MyAnnotation(message = "AAAAAAAAA")public Integer score;}在字段上标注该注解,然后编写一个main方法获取该注解的属性:
public static void main(String[] args) {Class<?> studentClass = Student.class;Field[] fields = studentClass.getDeclaredFields();//获取所有的类成员变量字段for (Field field : fields) {String fieldName = field.getName(); //获取该类成员变量的名字System.out.println("成员变量名是:" + fieldName);Annotation[] annotations = field.getAnnotations(); //获取该类成员变量上所有声明周期是运行时的注解for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType = annotation.annotationType();String annotationName = annotationType.getSimpleName();//注解的简短名称System.out.println(" 使用的注解是:" + annotationName);//判断该注解是不是 MyAnnotation 注解,是的话打印其 id 和 describe 属性if (annotationType.equals(MyAnnotation.class)) {MyAnnotation myAnnotation = field.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);String message = myAnnotation.message();System.out.println(" MyAnnotation注解中的message是:" + message);}}System.out.println();}} 执行后打印的内容: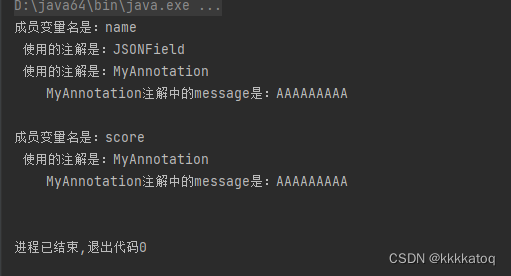
以上就是一个注解的简单实现。
四、使用切面执行自定义注解逻辑
在开发中一般加上注解之后会自动执行一些逻辑,大部分实现的原理是使用切面来实现注解的逻辑的。
1) 首先将刚才的注解修改成放在方法上的:
//注解用于方法
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
//运行时使用
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {String message() default "aaa";}2) 定义一个切面类:
@Component
@Aspect
@Slf4j
public class MyAnnotationAspect {/** 这是一个切入点* */@Pointcut("@annotation(com.redis.demo.aaa.annotation.MyAnnotation)")public void cutMethod(){}@Around("cutMethod() && @annotation(myAnnotation)")public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint point, MyAnnotation myAnnotation) {//获取方法名称Signature methodName = point.getSignature();//日志输出log.info(methodName+"进来了");Long l1=System.currentTimeMillis();Object obj=null;try {obj= point.proceed(point.getArgs());} catch (Throwable e) {e.printStackTrace();}log.info(methodName+"bye"+"\t耗時 "+(System.currentTimeMillis()-l1)+"\t"+myAnnotation.message());//记录一个耗时时间,将证明日志通知return obj;}}
