广东建设工程造价管理协会网站百度一下官方网址
文章目录
- day31 整数矩阵及其运算
- 面向对象思想
- java异常处理
- java中的getter和setter方法
- 代码
day31 整数矩阵及其运算
面向对象思想
结合之前day7和day8面向过程开发,只关注了矩阵加法和矩阵乘法的功能。而day31是面向对象开发,一个矩阵类,在这个类对象中包含有矩阵的加法,乘法,获取数据等功能(如add,multiply方法)。同时通过get,set方法来让用户通过方法获取类相关数据(getData,getRows,getColumns,setValue等),而非直接获取数据。在IntMatrix类,方法名为add的有两个,但这两个方法的区别在于传参以及返回不同,这体现了方法重载。
面向对象的三大特点(定义的描述来自百度):
- 封装:
(1)定义:将数据和对数据的操作封装在一个对象内部,对外部隐藏对象的实现细节,保证了程序的安全性和可靠性。
(2)IntMatrix类就体现了封装性,将数据和相关的操作封装在对象内部,我们对外只提供相应饿方法,如我们调用矩阵相乘就可以直接调用multiply方法即可 - 继承
(1)定义:通过定义父类和子类,子类可以继承父类的属性和方法,减少代码重复,提高代码的可维护性 - 多态
(1)定义:同一个方法可以根据不同的对象调用不同的实现方式,从而提高代码的灵活性和可扩展性。多态一般是通过继承或接口来实现的
java异常处理
在之前写哈夫曼树时已经涉及异常处理了,java的异常处理方法
-
try-catch-finally: 将可能要出现异常的代码放入try中,catch 捕获 try 中的异常,并处理,不管有没有异常,finally中的代码都会执行。(finally不是必须)
-
throw: 一般是语句抛出一个异常, 一般是手动抛出,并且可以抛出更为明确的异常
-
throws:一般是方法抛出一个异常,在方法后面声明异常(表示该方法可能会产生异常)
java中的getter和setter方法
一般在创建java实体类时,会把类相关属性设置为私有private(这是从安全角度去考虑),想要获取或设置这些私有属性可以通过方法去获取或设置,即getXXX,setXXX,而不是直接去操作这一个变量。这也体现了java的一大特点:封装性。
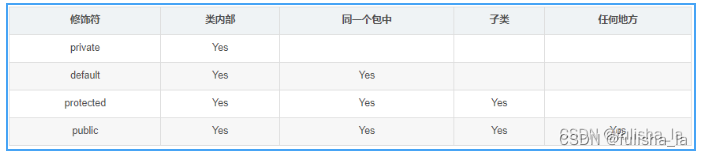
访问权限修饰符(private,procted,public,default)不同的访问权限,访问的范围不一样(从网上找了一个这样的图)
在项目中使用lombok可以减少写getter/setter/toString等方法的编写
代码
package matrix;
import java.util.Arrays;
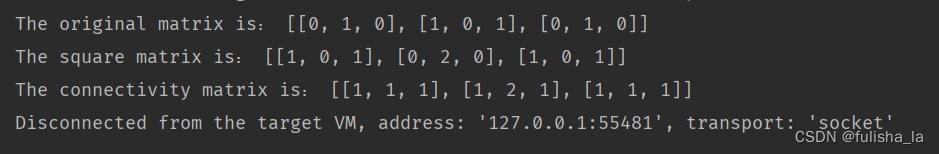
public class IntMatrix {int[][] data;/*** The first constructor.* @param paraRows The number of rows* @param paraColumns The number of columns*/public IntMatrix(int paraRows, int paraColumns){data = new int[paraRows][paraColumns];}/*** The second constructor. Construct a copy of the given matrix.* @param paraMatrix The given matrix.*/public IntMatrix(int[][] paraMatrix){data = new int[paraMatrix.length][paraMatrix[0].length];for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < data[0].length; j++) {data[i][j] = paraMatrix[i][j];}}}/*** The third constructor. Construct a copy of the given matrix.* @param paraMatrix The given matrix.*/public IntMatrix(IntMatrix paraMatrix) {this(paraMatrix.getData());}/*** Get identity matrix. The values at the diagonal are all 1* @param paraRows* @return*/public static IntMatrix getIdentityMatrix(int paraRows) {IntMatrix resultMatrix = new IntMatrix(paraRows, paraRows);for (int i = 0; i < paraRows; i++) {// According to access control, resultMatrix.data can be visitedresultMatrix.data[i][i] = 1;}return resultMatrix;}/*** Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.* @return*/@Overridepublic String toString() {return Arrays.deepToString(data);}/*** Get my data. Warning, the reference to the data instead of a copy of the data is returned.* @return*/public int[][] getData() {return data;}public int getRows() {return data.length;}public int getColumns() {return data[0].length;}/*** Set one the value of one element.* @param paraRow The row of the element.* @param paraColumn The column of the element.* @param paraValue The new value.*/public void setValue(int paraRow, int paraColumn, int paraValue){data[paraRow][paraColumn] = paraValue;}/*** Get the value of one element.* @param paraRow The row of the element.* @param paraColumn The column of the element.* @return*/public int getValue(int paraRow, int paraColumn) {return data[paraRow][paraColumn];}/*** Add another matrix to me.* @param paraMatrix The other matrix.* @throws Exception*/public void add(IntMatrix paraMatrix) throws Exception {// Step 1. Get the data of the given matrix.int[][] tempData = paraMatrix.getData();// Step 2. Size check.if (data.length != tempData.length) {throw new Exception("Cannot add matrices. Rows not match: " + data.length + " vs. "+ tempData.length + ".");}if (data[0].length != tempData[0].length) {throw new Exception("Cannot add matrices. Rows not match: " + data[0].length + " vs. "+ tempData[0].length + ".");}// Step 3. Add to me.for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < data[0].length; j++) {data[i][j] += tempData[i][j];}}}/*** Add two existing matrices.* @param paraMatrix1 The first matrix.* @param paraMatrix2 The second matrix.* @return A new matrix.* @throws Exception*/public static IntMatrix add(IntMatrix paraMatrix1, IntMatrix paraMatrix2) throws Exception {// Step 1. Clone the first matrix.IntMatrix resultMatrix = new IntMatrix(paraMatrix1);// Step 2. Add the second one.resultMatrix.add(paraMatrix2);return resultMatrix;}/*** Multiply two existing matrices.* @param paraMatrix1 The first matrix.* @param paraMatrix2 The second matrix.* @return A new matrix.* @throws Exception*/public static IntMatrix multiply(IntMatrix paraMatrix1, IntMatrix paraMatrix2) throws Exception {// Step 1. Check size.int[][] tempData1 = paraMatrix1.getData();int[][] tempData2 = paraMatrix2.getData();if (tempData1[0].length != tempData2.length) {throw new Exception("Cannot multiply matrices: " + tempData1[0].length + " vs. "+ tempData2.length + ".");}// Step 2. Allocate space.int[][] resultData = new int[tempData1.length][tempData2[0].length];// Step 3. Multiply.for (int i = 0; i < tempData1.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < tempData2[0].length; j++) {for (int k = 0; k < tempData1[0].length; k++) {resultData[i][j] += tempData1[i][k] * tempData2[k][j];}}}// Step 4. Construct the matrix object.IntMatrix resultMatrix = new IntMatrix(resultData);return resultMatrix;}public static void main(String args[]) {IntMatrix tempMatrix1 = new IntMatrix(3, 3);tempMatrix1.setValue(0, 1, 1);tempMatrix1.setValue(1, 0, 1);tempMatrix1.setValue(1, 2, 1);tempMatrix1.setValue(2, 1, 1);System.out.println("The original matrix is: " + tempMatrix1);IntMatrix tempMatrix2 = null;try {tempMatrix2 = IntMatrix.multiply(tempMatrix1, tempMatrix1);} catch (Exception ee) {System.out.println(ee);}System.out.println("The square matrix is: " + tempMatrix2);IntMatrix tempMatrix3 = new IntMatrix(tempMatrix2);try {tempMatrix3.add(tempMatrix1);} catch (Exception ee) {System.out.println(ee);}System.out.println("The connectivity matrix is: " + tempMatrix3);}
}