web是网站设计和建设吗搜什么关键词能找到网站
C语言函数大全
本篇介绍C语言函数大全-- t 开头的函数
1. tan,tanf,tanl
1.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double tan(double x) | 计算 以弧度 x 为单位的角度的正切值(double) |
float tanf(float x) | 计算 以弧度 x 为单位的角度的正切值(float) |
long double tanl(long double x) | 计算 以弧度 x 为单位的角度的正切值(long double) |
1.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>int main()
{double x = 45.0;double tan_value = tan(x * M_PI / 180.0);printf("The tangent of %lf degrees is %lf\n", x, tan_value);float xf = 60.0f;float tan_valuef = tanf(xf * M_PI / 180.0f);printf("The tangent of %f degrees is %f\n", xf, tan_valuef);long double xL = 30.0l;long double tan_valueL = tanl(xL * M_PI / 180.0l);printf("The tangent of %Lf degrees is %Lf\n", xL, tan_valueL);return 0;
}
1.3 运行结果
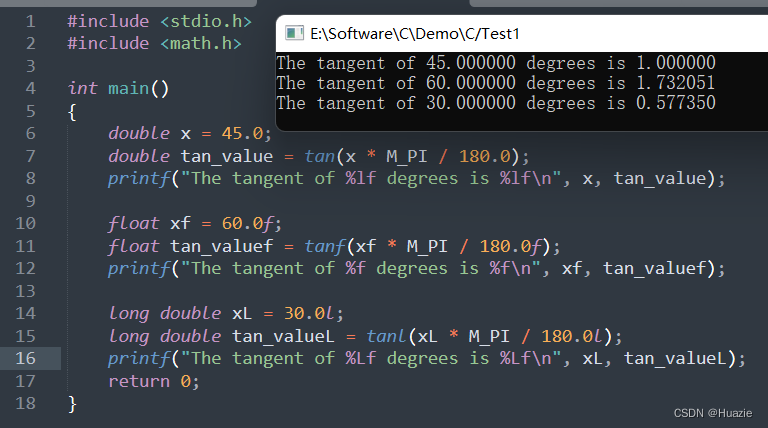
2. tanh,tanhf,tanhl
2.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double tanh(double x); | 计算 x 的双曲正切值(double) |
float tanhf(float x); | 计算 x 的双曲正切值(float) |
long double tanhl(long double x); | 计算 x 的双曲正切值(long double) |
2.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>int main()
{double x = 1.0;double tan_value = tanh(x);printf("%lf 的双曲正切值是 %lf\n", x, tan_value);float y = 2.0f;float tanh_value = tanhf(y);printf("%f 的双曲正切值是 %f\n", y, tanh_value);long double z = 3.0l;long double tanhl_value = tanhl(z);printf("%Lf 的双曲正切值是 %Lf\n", z, tanhl_value);return 0;
}
2.3 运行结果
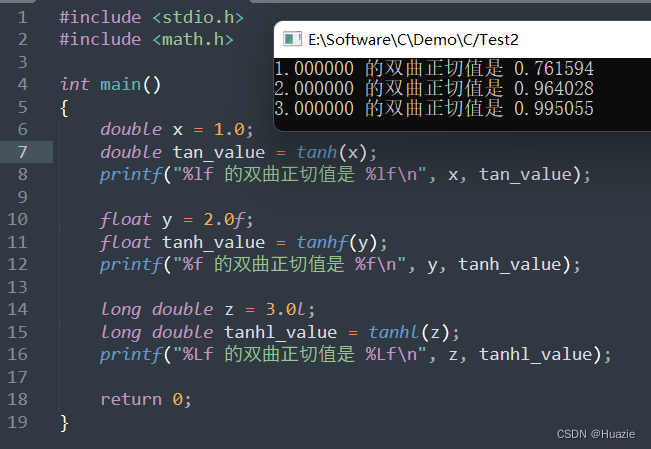
3. tell
3.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
off_t tell(int fd); | 用于返回文件指针当前位置相对于文件开头的偏移量 |
参数:
- fd : 是文件描述符,表示要查询的文件
3.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main()
{char buf[100];int fd = open("test.txt", O_RDONLY);off_t offset = tell(fd);printf("当前的文件偏移量是 %ld\n", offset);int nread = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));offset = tell(fd);printf("读取了 %d 个字节后,文件偏移量是 %ld\n", nread, offset);close(fd);return 0;
}
在上面这个示例中,
- 首先我们打开了一个名为 test.txt 的文件,并使用
tell()函数获取了当前的文件偏移量。 - 然后我们用
read()函数读取了一些数据,并再次使用tell()函数来获取新的文件偏移量。 - 最后我们使用
close()函数关闭文件。
注意:
tell()函数和lseek函数的功能类似,但有一个重要的区别:tell()函数只用于查询当前位置,而不能修改文件指针的位置。如果要修改文件指针的位置,请使用lseek()函数。
下面我们来看看,使用 lseek() 函数来演示上面的 tell() 函数的示例 :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main()
{char buf[100];int fd = open("test.txt", O_RDONLY);off_t offset = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_CUR);printf("当前的文件偏移量是 %ld\n", offset);int nread = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));offset = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_CUR);printf("读取了 %d 个字节后,文件偏移量是 %ld\n", nread, offset);close(fd);return 0;
}
3.3 运行结果
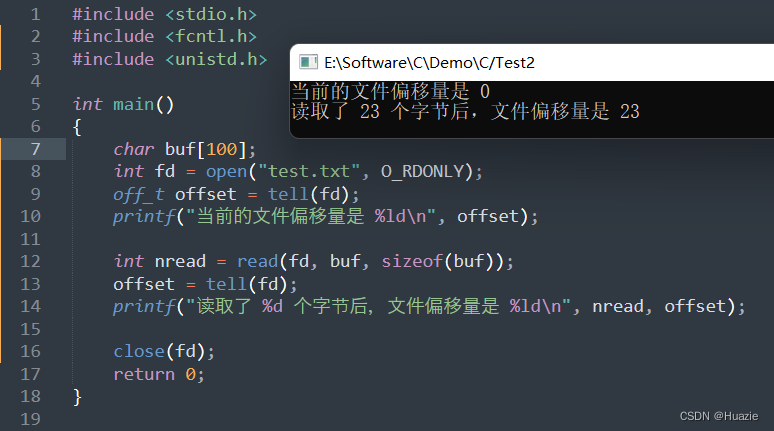
4. telldir
4.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
long int telldir(DIR *dirp); | 获取目录流的当前位置 |
参数:
- dirp : 指向
DIR类型结构体的指针
4.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dirent.h>int main()
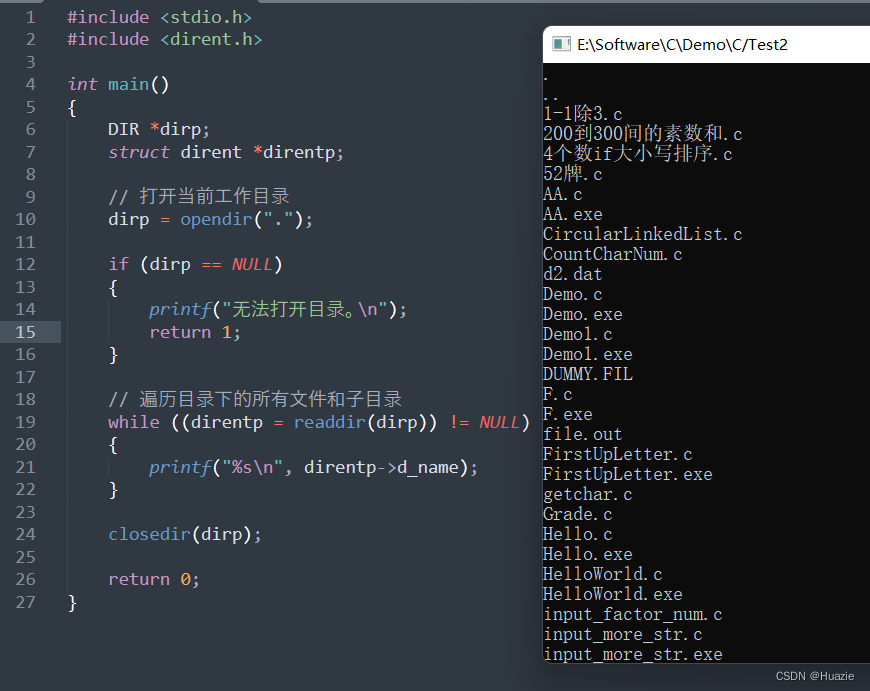
{DIR *dirp;struct dirent *direntp;// 打开当前工作目录dirp = opendir(".");if (dirp == NULL) {printf("无法打开目录。\n");return 1;}// 遍历目录下的所有文件和子目录while ((direntp = readdir(dirp)) != NULL) {printf("%s\n", direntp->d_name);}closedir(dirp);return 0;
}
4.3 运行结果
5. textheight,textwidth
5.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int textheight(char *string); | 用于获取当前文本模式下字符的高度 |
int textwidth(char *string); | 用于获取当前文本模式下字符的宽度 |
参数:
- string : 要查询的字符串
5.2 演示示例
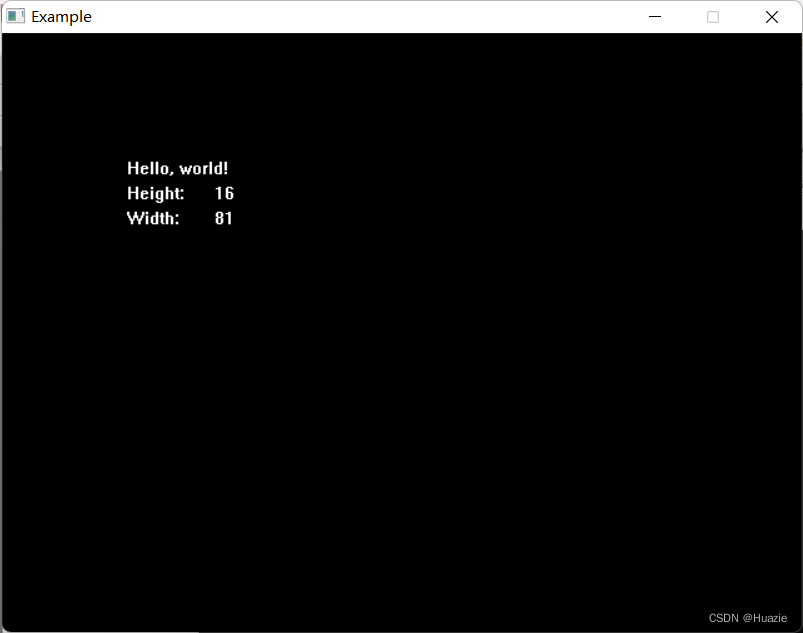
#include <graphics.h>int main() {initwindow(640, 480, "Example");char str[] = "Hello, world!";int height = textheight(str); // 当前文本模式下字符的高度int width = textwidth(str); // 当前文本模式下字符的宽度outtextxy(100, 100, str);outtextxy(100, 120, "Height: ");outtextxy(170, 120, itoa(height, str, 10));outtextxy(100, 140, "Width: ");outtextxy(170, 140, itoa(width, str, 10));getch();closegraph();return 0;
}
5.3 运行结果
6. time
6.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
time_t time(time_t *timer); | 可以用于获取从 1970 年 1 月 1 日 00:00:00 UTC 到当前时间的秒数 |
参数:
- timer : 一个指向
time_t类型对象的指针,如果不想使用此参数,可以将它设置为NULL
6.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>int main()
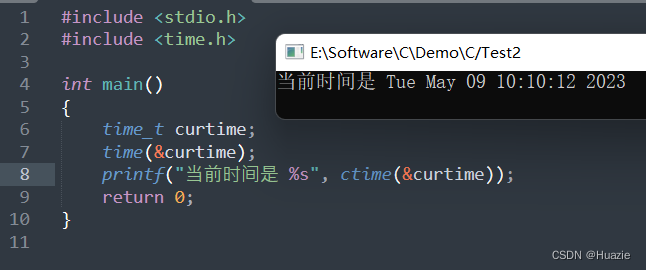
{time_t curtime;time(&curtime);printf("当前时间是 %s", ctime(&curtime));return 0;
}
在上面的示例中,
- 首先我们使用
time()函数来获取当前时间的秒数; - 然后使用
ctime()函数将其转换为可读的日期和时间格式; - 最后,再用将日期和时间字符串输出到标准输出流中。
6.3 运行结果
7. tmpfile
7.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
FILE *tmpfile(void); | 可以用于在临时目录中创建一个唯一的临时文件,并返回文件指针 |
7.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>int main()
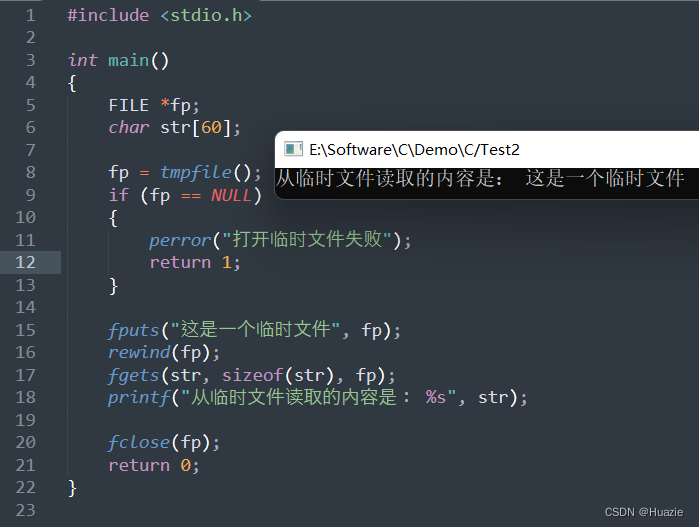
{FILE *fp;char str[60];fp = tmpfile();if (fp == NULL) {perror("打开临时文件失败");return 1;}fputs("这是一个临时文件", fp);rewind(fp);fgets(str, sizeof(str), fp);printf("从临时文件读取的内容是: %s", str);fclose(fp);return 0;
}
7.3 运行结果
在上述的示例中,
- 首先我们使用
tmpfile()函数创建一个临时文件; - 接着使用
fputs()函数将字符串"这是一个临时文件"写入该文件; - 然后,我们使用
rewind()函数将文件指针移动到文件开始处; - 再接着,使用
fgets()函数从临时文件中读取数据并将其存储到字符串数组str中; - 最后,我们输出从临时文件中读取的数据,并关闭临时文件。
注意: 使用
tmpfile()创建的临时文件只在程序运行期间存在,并在程序终止时自动删除。如果需要在程序运行期间保留临时文件,请使用tmpnam()或mkstemp()等函数来创建文件。
8. tmpnam
8.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
char *tmpnam(char *s); | 用于创建一个唯一的临时文件名 |
参数:
- s : 一个指向字符数组的指针,用于存储临时文件名。如果
s等于NULL,则函数会返回指向静态内存区的指针,该内存区包含了唯一的临时文件名
8.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>int main()
{char tmpname[L_tmpnam];char *filename;filename = tmpnam(tmpname);printf("临时文件名是:%s\n", filename);return 0;
}
在上面的示例中,
- 我们首先使用
tmpnam()函数创建一个唯一的临时文件名; - 然后将其存储到字符数组
tmpname中; - 最后,我们输出该临时文件名。
注意: 使用
tmpnam()创建的临时文件名只在程序运行期间存在,不具有真正唯一性,因此可能存在一定程度的风险。如果需要创建一个具有真正唯一性的临时文件,请考虑使用mkstemp()或类似的函数。
8.3 运行结果
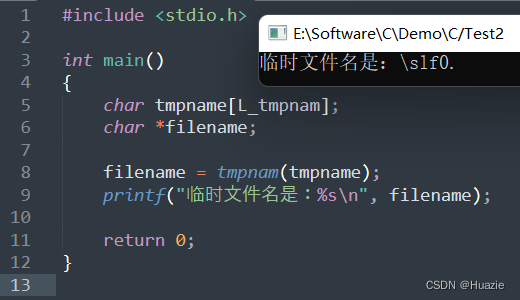
9. toascii
9.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int toascii(int c); | 将一个字符转换为其对应的 ASCII 码值 |
参数:
- c : 要转换的字符
9.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>int main()
{char ch = 'A';// 将字符转换为其对应的 ASCII 码值int ascii_val = toascii(ch);printf("字符 %c 的 ASCII 码值为 %d\n", ch, ascii_val);return 0;
}
注意 :
toascii()函数已经过时,不建议在新代码中使用。在C99标准中,改用更安全的isascii()函数来检查字符是否为7-bit ASCII字符,并使用位掩码操作或其他算法来将非ASCII字符转换为相应的7-bit ASCII码值。
知识点:
7-bit ASCII,也称为美国信息交换标准代码 (American Standard Code for Information Interchange),是一种基于英语的字符编码系统,使用7个二进制位(即一个字节)表示每个字符。它涵盖了拉丁字母、数字、标点符号和一些特殊符号,共计128个字符。
9.3 运行结果
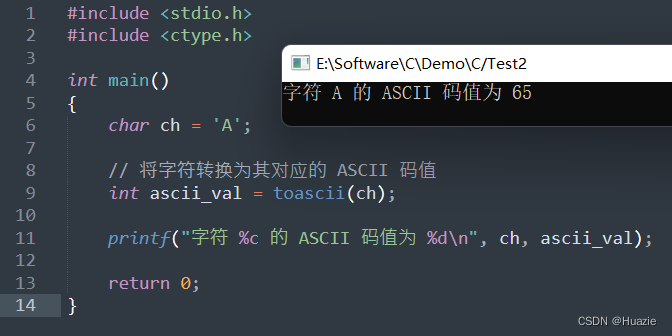
10. tolower
10.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int tolower(int c); | 可以用于将一个 ASCII 字符转换为小写字母 |
参数:
- c : 要转换的字符
10.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>int main()
{char str[] = "Hello, World!";int i = 0;printf("转换前字符串: %s\n", str);printf("转换后字符串: ");while (str[i]) {putchar(tolower(str[i]));i++;}return 0;
}
10.3 运行结果
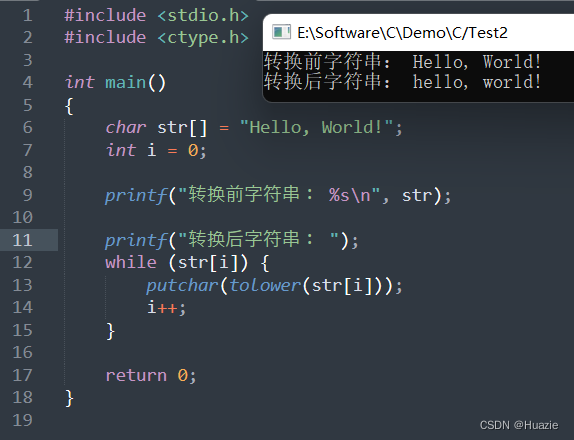
11. toupper
11.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int toupper(int c); | 可以用于将一个 ASCII 字符转换为大写字母 |
参数:
- c : 要转换的字符
11.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>int main()
{char str[] = "Hello, World!";int i = 0;printf("转换前字符串: %s\n", str);printf("转换后字符串: ");while (str[i]) {putchar(toupper(str[i]));i++;}return 0;
}
11.3 运行结果
12. trunc,truncf,truncl
12.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double trunc(double x); | 截取 x 的小数部分,并返回整数部分(double) |
float truncf(float x); | 截取 x 的小数部分,并返回整数部分(float) |
long double truncl(long double x); | 截取 x 的小数部分,并返回整数部分(long double) |
12.2 演示示例
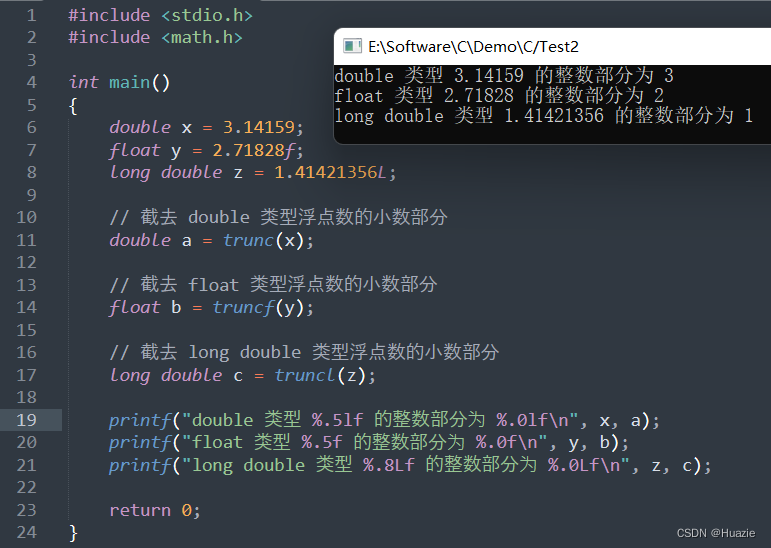
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>int main()
{double x = 3.14159;float y = 2.71828f;long double z = 1.41421356L;// 截去 double 类型浮点数的小数部分double a = trunc(x);// 截去 float 类型浮点数的小数部分float b = truncf(y);// 截去 long double 类型浮点数的小数部分long double c = truncl(z);printf("double 类型 %.5lf 的整数部分为 %.0lf\n", x, a);printf("float 类型 %.5f 的整数部分为 %.0f\n", y, b);printf("long double 类型 %.8Lf 的整数部分为 %.0Lf\n", z, c);return 0;
}
12.3 运行结果
13. tzset
13.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
void tzset(void); | 可以用于设置时区信息 |
参数:
13.2 演示示例
UNIX/Linux 下示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
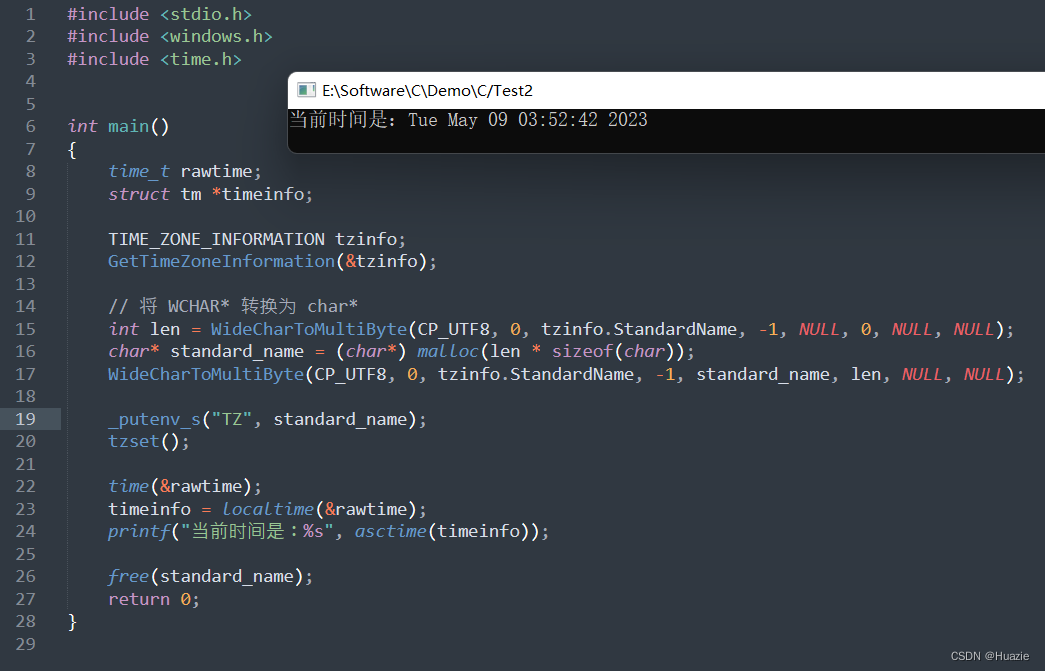
#include <time.h>#define _XOPEN_SOURCE 700int main()
{time_t rawtime;struct tm *timeinfo;// 设置时区为 UTCsetenv("TZ", "UTC", 1);tzset();time(&rawtime);timeinfo = localtime(&rawtime);printf("当前时间是:%s", asctime(timeinfo));return 0;
}
windows 下示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include <time.h>int main()
{time_t rawtime;struct tm *timeinfo;TIME_ZONE_INFORMATION tzinfo;GetTimeZoneInformation(&tzinfo);// 将 WCHAR* 转换为 char*int len = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_UTF8, 0, tzinfo.StandardName, -1, NULL, 0, NULL, NULL);char* standard_name = (char*) malloc(len * sizeof(char));WideCharToMultiByte(CP_UTF8, 0, tzinfo.StandardName, -1, standard_name, len, NULL, NULL);_putenv_s("TZ", standard_name);tzset();time(&rawtime);timeinfo = localtime(&rawtime);printf("当前时间是:%s", asctime(timeinfo));free(standard_name);return 0;
}
在上述示例代码中,
- 首先定义变量
rawtime和timeinfo,分别用于存储当前时间和时间结构体。 - 接着使用
GetTimeZoneInformation()函数获取当前系统时区信息,并将其存储在tzinfo变量中。 - 然后使用
WideCharToMultiByte()函数将tzinfo.StandardName转换为UTF-8编码的字符串,并将其存储在standard_name变量中。 - 再接着使用
putenv_s()函数将standard_name设置为环境变量TZ的值,并使用 tzset 函数更新本地时区信息。 - 再然后使用
localtime()函数将rawtime转换为时间结构体timeinfo。 - 之后使用
asctime()函数将时间结构体timeinfo转换为字符串格式,并输出到标准输出流中。 - 最后释放
standard_name分配的内存空间,并正常结束程序。
13.3 运行结果
14. tgamma,tgammaf,tgammal
14.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double tgamma(double x); | 用于计算 Gamma 函数(double) |
float tgammaf(float x); | 用于计算 Gamma 函数(float) |
long double tgammal(long double x); | 用于计算 Gamma 函数(long double) |
14.2 演示示例
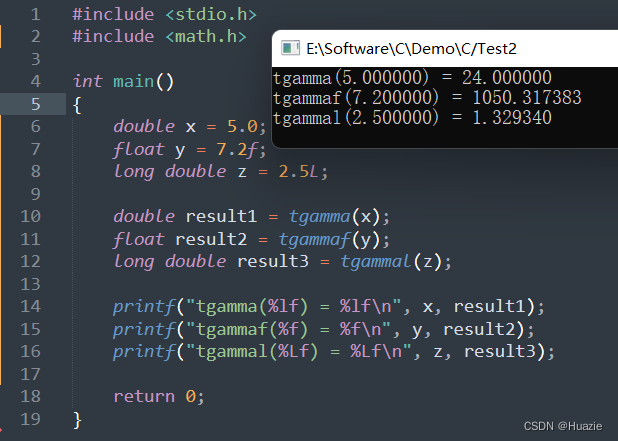
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>int main()
{double x = 5.0;float y = 7.2f;long double z = 2.5L;double result1 = tgamma(x);float result2 = tgammaf(y);long double result3 = tgammal(z);printf("tgamma(%lf) = %lf\n", x, result1);printf("tgammaf(%f) = %f\n", y, result2); printf("tgammal(%Lf) = %Lf\n", z, result3);return 0;
}
知识点: 伽玛函数(
Gamma函数),也叫欧拉第二积分,是阶乘函数在实数与复数上扩展的一类函数。
14.3 运行结果
参考
- [API Reference Document]
- [ASCII]
