专业简历制作软件seo工具在线访问
chatgpt在这一章表现的不好,所以我主要用它来帮我翻译文章+提炼信息
1.前言
首先找到spark官网里关于MLLib的链接
spark内一共有2种支持机器学习的包,
一种是spark.ml,基于DataFrame的,也是目前主流的
另一种则是spark.mllib,是基于RDD的,在维护,但不增加新特性了
所以这一节的学习以spark.ml中的pipeline为主。其他的和sklearn里的非常像,大家可以自己去看。
2.Pipeline介绍
基于DataFrame创建pipeline,对数据进行清洗/转换/训练。
2.1 Pipeline的构成
Pipeline主要分为:
1.Transformer,人如其名,就是对数据做转换的
2.Estimators,使用fit函数对数据做拟合,
2.2 Pipeline如何工作
pipeline是由一系列stage构成,而每一个stage则是由一个transformer或者是estimator构成。这些stage按顺序执行,将输入的DataFrame按相应的方式转换:Transformer对应的stage调用transform()函数,而Estimator对应的stage则调用fit函数取创建一个Transformer,(它成为PipelineModel或已拟合的Pipeline的一部分),然后在DataFrame上调用该Transformer的transform()方法。
有些绕,可以看看下面这张图:
对训练数据进行pipeline操作,对应的红框表示Estimator,使用训练数据拟合LR
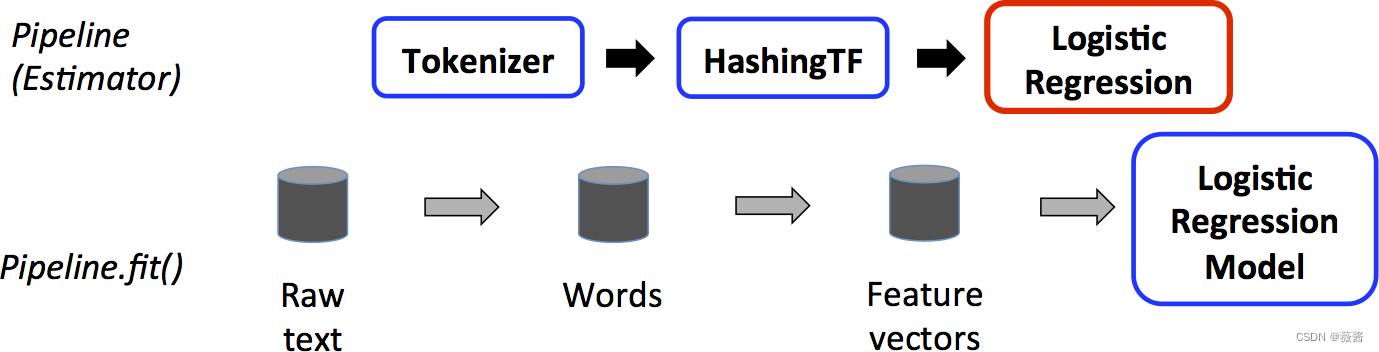
而对测试数据,对应的LR变成了蓝框,此时LR也成为了Transformer,对测试数据进行transform()操作。
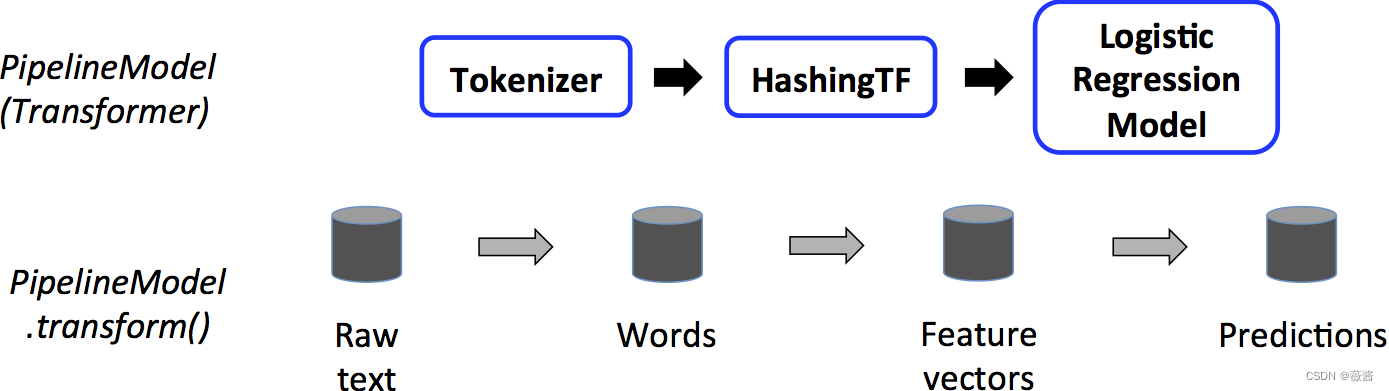
3.注意项
1.执行DAG图
上面展示的顺序执行pipeline的方式,实际上满足无环拓扑图也可以使用pipeline
2.参数
- 可以直接设置
lr.setMaxIter(10) - 在调用transform()或者fit时传入ParamMap
3.兼容性
不同版本的MLlib兼容性其实并不完全能保证的
主要版本:不能保证,但会尽力兼容。
小版本和补丁版本:是的,它们是向后兼容的。
4.代码参考:
4.1 Estimator, Transformer, and Param代码参考
from pyspark.ml.linalg import Vectors
from pyspark.ml.classification import LogisticRegression# Prepare training data from a list of (label, features) tuples.
training = spark.createDataFrame([(1.0, Vectors.dense([0.0, 1.1, 0.1])),(0.0, Vectors.dense([2.0, 1.0, -1.0])),(0.0, Vectors.dense([2.0, 1.3, 1.0])),(1.0, Vectors.dense([0.0, 1.2, -0.5]))], ["label", "features"])# Create a LogisticRegression instance. This instance is an Estimator.
lr = LogisticRegression(maxIter=10, regParam=0.01)
# Print out the parameters, documentation, and any default values.
print("LogisticRegression parameters:\n" + lr.explainParams() + "\n")# Learn a LogisticRegression model. This uses the parameters stored in lr.
model1 = lr.fit(training)# Since model1 is a Model (i.e., a transformer produced by an Estimator),
# we can view the parameters it used during fit().
# This prints the parameter (name: value) pairs, where names are unique IDs for this
# LogisticRegression instance.
print("Model 1 was fit using parameters: ")
print(model1.extractParamMap())# We may alternatively specify parameters using a Python dictionary as a paramMap
paramMap = {lr.maxIter: 20}
paramMap[lr.maxIter] = 30 # Specify 1 Param, overwriting the original maxIter.
# Specify multiple Params.
paramMap.update({lr.regParam: 0.1, lr.threshold: 0.55}) # type: ignore# You can combine paramMaps, which are python dictionaries.
# Change output column name
paramMap2 = {lr.probabilityCol: "myProbability"}
paramMapCombined = paramMap.copy()
paramMapCombined.update(paramMap2) # type: ignore# Now learn a new model using the paramMapCombined parameters.
# paramMapCombined overrides all parameters set earlier via lr.set* methods.
model2 = lr.fit(training, paramMapCombined)
print("Model 2 was fit using parameters: ")
print(model2.extractParamMap())# Prepare test data
test = spark.createDataFrame([(1.0, Vectors.dense([-1.0, 1.5, 1.3])),(0.0, Vectors.dense([3.0, 2.0, -0.1])),(1.0, Vectors.dense([0.0, 2.2, -1.5]))], ["label", "features"])# Make predictions on test data using the Transformer.transform() method.
# LogisticRegression.transform will only use the 'features' column.
# Note that model2.transform() outputs a "myProbability" column instead of the usual
# 'probability' column since we renamed the lr.probabilityCol parameter previously.
prediction = model2.transform(test)
result = prediction.select("features", "label", "myProbability", "prediction") \.collect()for row in result:print("features=%s, label=%s -> prob=%s, prediction=%s"% (row.features, row.label, row.myProbability, row.prediction))4.2 Pipeline 代码参考
from pyspark.ml import Pipeline
from pyspark.ml.classification import LogisticRegression
from pyspark.ml.feature import HashingTF, Tokenizer# Prepare training documents from a list of (id, text, label) tuples.
training = spark.createDataFrame([(0, "a b c d e spark", 1.0),(1, "b d", 0.0),(2, "spark f g h", 1.0),(3, "hadoop mapreduce", 0.0)
], ["id", "text", "label"])# Configure an ML pipeline, which consists of three stages: tokenizer, hashingTF, and lr.
tokenizer = Tokenizer(inputCol="text", outputCol="words")
hashingTF = HashingTF(inputCol=tokenizer.getOutputCol(), outputCol="features")
lr = LogisticRegression(maxIter=10, regParam=0.001)
pipeline = Pipeline(stages=[tokenizer, hashingTF, lr])# Fit the pipeline to training documents.
model = pipeline.fit(training)# Prepare test documents, which are unlabeled (id, text) tuples.
test = spark.createDataFrame([(4, "spark i j k"),(5, "l m n"),(6, "spark hadoop spark"),(7, "apache hadoop")
], ["id", "text"])# Make predictions on test documents and print columns of interest.
prediction = model.transform(test)
selected = prediction.select("id", "text", "probability", "prediction")
for row in selected.collect():rid, text, prob, prediction = rowprint("(%d, %s) --> prob=%s, prediction=%f" % (rid, text, str(prob), prediction # type: ignore))