万维网站注册网络销售平台排名前十
NMS和soft-nms算法
nms :iou阈值的作用,如果iou大于阈值,则认为是两个框是同一个物体,所以会删除分数小的框。
https://blog.csdn.net/eurus_/article/details/84251975
以此图为例,传统的NMS,首先选定一个IOU阈值,例如为0.25。然后将所有4个窗口(bounding box)按照得分由高到低排序。然后选中得分最高的窗口,遍历计算剩余的3个窗口与该窗口的重叠面积比例(IOU),如果IOU大于阈值0.25,则将窗口删除。然后,再从剩余的窗口中选中一个得分最高的,重复上述过程。直至所有窗口都被处理。
假如0.25是一个不错的阈值,那么我们可以得到比较好的结果,如下图:
如果,我们的IOU阈值设定的特别小,比如说0.1。那么2个人的窗口会被归为一个人而被融合。得到下面的错误结果:
如果,我们的IOU阈值设定的特别大,比如说0.6。那么又可能得到下面的错误结果
soft nms 对多个小目标效果不好
https://blog.csdn.net/mooneve/article/details/100537621
import numpy as npdef soft_nms(dets, sigma=0.5, Nt=0.5, method=2, threshold=0.1):box_len = len(dets) # box的个数for i in range(box_len):tmpx1, tmpy1, tmpx2, tmpy2, ts = dets[i, 0], dets[i, 1], dets[i, 2], dets[i, 3], dets[i, 4]max_pos = imax_scores = ts# get max boxpos = i+1while pos < box_len:if max_scores < dets[pos, 4]:max_scores = dets[pos, 4]max_pos = pospos += 1# add max box as a detectiondets[i, :] = dets[max_pos, :]# swap ith box with position of max boxdets[max_pos, 0] = tmpx1dets[max_pos, 1] = tmpy1dets[max_pos, 2] = tmpx2dets[max_pos, 3] = tmpy2dets[max_pos, 4] = ts# 将置信度最高的 box 赋给临时变量tmpx1, tmpy1, tmpx2, tmpy2, ts = dets[i, 0], dets[i, 1], dets[i, 2], dets[i, 3], dets[i, 4]pos = i+1# NMS iterations, note that box_len changes if detection boxes fall below thresholdwhile pos < box_len:x1, y1, x2, y2 = dets[pos, 0], dets[pos, 1], dets[pos, 2], dets[pos, 3]area = (x2 - x1 + 1)*(y2 - y1 + 1)iw = (min(tmpx2, x2) - max(tmpx1, x1) + 1)ih = (min(tmpy2, y2) - max(tmpy1, y1) + 1)if iw > 0 and ih > 0:overlaps = iw * ihious = overlaps / ((tmpx2 - tmpx1 + 1) * (tmpy2 - tmpy1 + 1) + area - overlaps)if method == 1: # 线性if ious > Nt:weight = 1 - iouselse:weight = 1elif method == 2: # gaussianweight = np.exp(-(ious**2) / sigma)else: # original NMSif ious > Nt:weight = 0else:weight = 1# 赋予该box新的置信度dets[pos, 4] = weight * dets[pos, 4]# 如果box得分低于阈值thresh,则通过与最后一个框交换来丢弃该框if dets[pos, 4] < threshold:dets[pos, 0] = dets[box_len-1, 0]dets[pos, 1] = dets[box_len-1, 1]dets[pos, 2] = dets[box_len-1, 2]dets[pos, 3] = dets[box_len-1, 3]dets[pos, 4] = dets[box_len-1, 4]box_len = box_len-1pos = pos-1pos += 1keep = [i for i in range(box_len)]return keepif __name__ == '__main__':dets = [[0, 0, 100, 101, 0.9], [5, 6, 90, 110, 0.7], [17, 19, 80, 120, 0.8], [10, 8, 115, 105, 0.5]]dets = np.array(dets)result = soft_nms(dets, 0.5)print(result)原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/zf-blog/p/8532228.html
这篇也有代码:
https://blog.csdn.net/e01528/article/details/80800122
https://www.cnblogs.com/makefile/p/nms.html
这个是需要编译的;
http://www.cnblogs.com/king-lps/p/9031568.html
非极大值抑制算法(nms)
1. 算法原理
非极大值抑制算法(Non-maximum suppression, NMS)的本质是搜索局部极大值,抑制非极大值元素。
2. 3邻域情况下NMS的实现
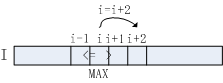
3邻域情况下的NMS即判断一维数组I[W]的元素I[i](2<=i<=W-1)是否大于其左邻元素I[i-1]和右邻元素I[i+1],算法流程如下图所示:

a. 算法流程3-5行判断当前元素是否大于其左邻与右邻元素,如符合条件,该元素即为极大值点。对于极大值点I[i],已知I[i]>I[i+1],故无需对i+1位置元素做进一步处理,直接跳至i+2位置,对应算法流程第12行。
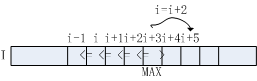
b. 若元素I[i]不满足算法流程第3行判断条件,将其右邻I[i+1]作为极大值候选,对应算法流程第7行。采用单调递增的方式向右查找,直至找到满足I[i]>I[i+1]的元素,若i<=W-1,该点即为极大值点,对应算法流程第10-11行。
3. NMS在物体检测中的应用
物体检测中应用NMS算法的主要目的是消除多余(交叉重复)的窗口,找到最佳物体检测位置。
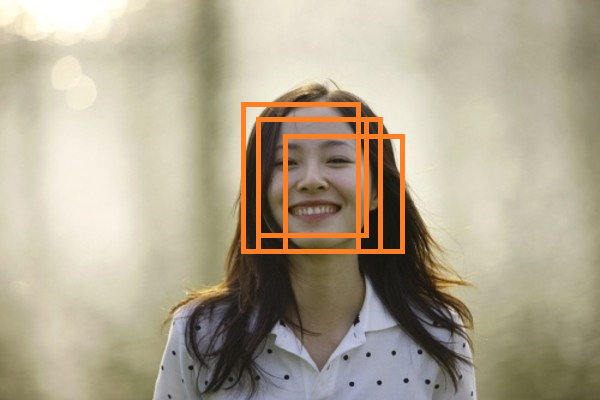
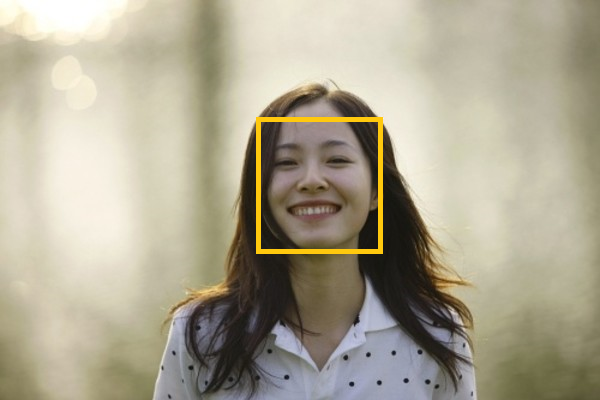
如上图所示,人脸检测中,虽然每个窗口均检测到人脸,但仅需给出一个最有可能表征人脸的窗口
程序整体思路:
先将box中的数据分别存入x1,y1,x2,y2,s中,分别为坐标和置信度,算出每个框的面积,存入area,基于置信度s,从小到达进行排序,做一个while循环,取出置信度最高的,即排序后的最后一个,然后将该框进行保留,存入pick中,然后和其他所有的框进行比对,大于规定阈值就将别的框去掉,并将该置信度最高的框和所有比对过程,大于阈值的框存入suppress,for循环后,将I中满足suppress条件的置为空。直到I为空退出while。
代码(C++):

static void sort(int n, const float* x, int* indices)
{
// 排序函数(降序排序),排序后进行交换的是indices中的数据
// n:排序总数// x:带排序数// indices:初始为0~n-1数目 int i, j; for (i = 0; i < n; i++) for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { if (x[indices[j]] > x[indices[i]]) { //float x_tmp = x[i]; int index_tmp = indices[i]; //x[i] = x[j]; indices[i] = indices[j]; //x[j] = x_tmp; indices[j] = index_tmp; } }
}

int nonMaximumSuppression(int numBoxes, const CvPoint *points, const CvPoint *oppositePoints, const float *score, float overlapThreshold, int *numBoxesOut, CvPoint **pointsOut, CvPoint **oppositePointsOut, float **scoreOut)
{ // numBoxes:窗口数目// points:窗口左上角坐标点// oppositePoints:窗口右下角坐标点
// score:窗口得分// overlapThreshold:重叠阈值控制// numBoxesOut:输出窗口数目
// pointsOut:输出窗口左上角坐标点// oppositePoints:输出窗口右下角坐标点
// scoreOut:输出窗口得分 int i, j, index; float* box_area = (float*)malloc(numBoxes * sizeof(float)); // 定义窗口面积变量并分配空间 int* indices = (int*)malloc(numBoxes * sizeof(int)); // 定义窗口索引并分配空间 int* is_suppressed = (int*)malloc(numBoxes * sizeof(int)); // 定义是否抑制表标志并分配空间 // 初始化indices、is_supperssed、box_area信息 for (i = 0; i < numBoxes; i++) { indices[i] = i; is_suppressed[i] = 0; box_area[i] = (float)( (oppositePoints[i].x - points[i].x + 1) * (oppositePoints[i].y - points[i].y + 1)); } // 对输入窗口按照分数比值进行排序,排序后的编号放在indices中 sort(numBoxes, score, indices); for (i = 0; i < numBoxes; i++) // 循环所有窗口 { if (!is_suppressed[indices[i]]) // 判断窗口是否被抑制 { for (j = i + 1; j < numBoxes; j++) // 循环当前窗口之后的窗口 { if (!is_suppressed[indices[j]]) // 判断窗口是否被抑制 { int x1max = max(points[indices[i]].x, points[indices[j]].x); // 求两个窗口左上角x坐标最大值 int x2min = min(oppositePoints[indices[i]].x, oppositePoints[indices[j]].x); // 求两个窗口右下角x坐标最小值 int y1max = max(points[indices[i]].y, points[indices[j]].y); // 求两个窗口左上角y坐标最大值 int y2min = min(oppositePoints[indices[i]].y, oppositePoints[indices[j]].y); // 求两个窗口右下角y坐标最小值 int overlapWidth = x2min - x1max + 1; // 计算两矩形重叠的宽度 int overlapHeight = y2min - y1max + 1; // 计算两矩形重叠的高度 if (overlapWidth > 0 && overlapHeight > 0) { float overlapPart = (overlapWidth * overlapHeight) / box_area[indices[j]]; // 计算重叠的比率 if (overlapPart > overlapThreshold) // 判断重叠比率是否超过重叠阈值 { is_suppressed[indices[j]] = 1; // 将窗口j标记为抑制 } } } } } } *numBoxesOut = 0; // 初始化输出窗口数目0 for (i = 0; i < numBoxes; i++) { if (!is_suppressed[i]) (*numBoxesOut)++; // 统计输出窗口数目 } *pointsOut = (CvPoint *)malloc((*numBoxesOut) * sizeof(CvPoint)); // 分配输出窗口左上角坐标空间 *oppositePointsOut = (CvPoint *)malloc((*numBoxesOut) * sizeof(CvPoint)); // 分配输出窗口右下角坐标空间 *scoreOut = (float *)malloc((*numBoxesOut) * sizeof(float)); // 分配输出窗口得分空间 index = 0; for (i = 0; i < numBoxes; i++) // 遍历所有输入窗口 { if (!is_suppressed[indices[i]]) // 将未发生抑制的窗口信息保存到输出信息中 { (*pointsOut)[index].x = points[indices[i]].x; (*pointsOut)[index].y = points[indices[i]].y; (*oppositePointsOut)[index].x = oppositePoints[indices[i]].x; (*oppositePointsOut)[index].y = oppositePoints[indices[i]].y; (*scoreOut)[index] = score[indices[i]]; index++; } } free(indices); // 释放indices空间 free(box_area); // 释放box_area空间 free(is_suppressed); // 释放is_suppressed空间 return LATENT_SVM_OK;
} 
软化非极大值抑制算法(softnms)
参考链接:http://blog.csdn.net/app_12062011/article/details/77963494
Motivation
绝大部分目标检测方法,最后都要用到 NMS-非极大值抑制进行后处理。 通常的做法是将检测框按得分排序,然后保留得分最高的框,同时删除与该框重叠面积大于一定比例的其它框。
这种贪心式方法存在如下图所示的问题: 红色框和绿色框是当前的检测结果,二者的得分分别是0.95和0.80。如果按照传统的NMS进行处理,首先选中得分最高的红色框,然后绿色框就会因为与之重叠面积过大而被删掉。
另一方面,NMS的阈值也不太容易确定,设小了会出现下图的情况(绿色框因为和红色框重叠面积较大而被删掉),设置过高又容易增大误检。

思路:不要粗鲁地删除所有IOU大于阈值的框,而是降低其置信度。
Method
先直接上伪代码,如下图:如文章题目而言,就是用一行代码来替换掉原来的NMS。按照下图整个处理一遍之后,指定一个置信度阈值,然后最后得分大于该阈值的检测框得以保留

原来的NMS可以描述如下:将IOU大于阈值的窗口的得分全部置为0。

文章的改进有两种形式,一种是线性加权的:

一种是高斯加权的:

分析上面的两种改进形式,思想都是:M为当前得分最高框, 为待处理框, 和M的IOU越大, 的得分 就下降的越厉害。
具体地,下面是作者给出的代码:(当然不止一行T_T)

def cpu_soft_nms(np.ndarray[float, ndim=2] boxes, float sigma=0.5, float Nt=0.3, float threshold=0.001, unsigned int method=0):cdef unsigned int N = boxes.shape[0]cdef float iw, ih, box_areacdef float uacdef int pos = 0cdef float maxscore = 0cdef int maxpos = 0cdef float x1,x2,y1,y2,tx1,tx2,ty1,ty2,ts,area,weight,ovfor i in range(N):maxscore = boxes[i, 4]maxpos = itx1 = boxes[i,0]ty1 = boxes[i,1]tx2 = boxes[i,2]ty2 = boxes[i,3]ts = boxes[i,4]pos = i + 1# get max boxwhile pos < N:if maxscore < boxes[pos, 4]:maxscore = boxes[pos, 4]maxpos = pospos = pos + 1# add max box as a detection boxes[i,0] = boxes[maxpos,0]boxes[i,1] = boxes[maxpos,1]boxes[i,2] = boxes[maxpos,2]boxes[i,3] = boxes[maxpos,3]boxes[i,4] = boxes[maxpos,4]# swap ith box with position of max boxboxes[maxpos,0] = tx1boxes[maxpos,1] = ty1boxes[maxpos,2] = tx2boxes[maxpos,3] = ty2boxes[maxpos,4] = tstx1 = boxes[i,0]ty1 = boxes[i,1]tx2 = boxes[i,2]ty2 = boxes[i,3]ts = boxes[i,4]pos = i + 1# NMS iterations, note that N changes if detection boxes fall below thresholdwhile pos < N:x1 = boxes[pos, 0]y1 = boxes[pos, 1]x2 = boxes[pos, 2]y2 = boxes[pos, 3]s = boxes[pos, 4]area = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)iw = (min(tx2, x2) - max(tx1, x1) + 1)if iw > 0:ih = (min(ty2, y2) - max(ty1, y1) + 1)if ih > 0:ua = float((tx2 - tx1 + 1) * (ty2 - ty1 + 1) + area - iw * ih)ov = iw * ih / ua #iou between max box and detection boxif method == 1: # linearif ov > Nt: weight = 1 - ovelse:weight = 1elif method == 2: # gaussianweight = np.exp(-(ov * ov)/sigma)else: # original NMSif ov > Nt: weight = 0else:weight = 1boxes[pos, 4] = weight*boxes[pos, 4]# if box score falls below threshold, discard the box by swapping with last box# update Nif boxes[pos, 4] < threshold:boxes[pos,0] = boxes[N-1, 0]boxes[pos,1] = boxes[N-1, 1]boxes[pos,2] = boxes[N-1, 2]boxes[pos,3] = boxes[N-1, 3]boxes[pos,4] = boxes[N-1, 4]N = N - 1pos = pos - 1pos = pos + 1keep = [i for i in range(N)]return keep
这么做的解释如下:
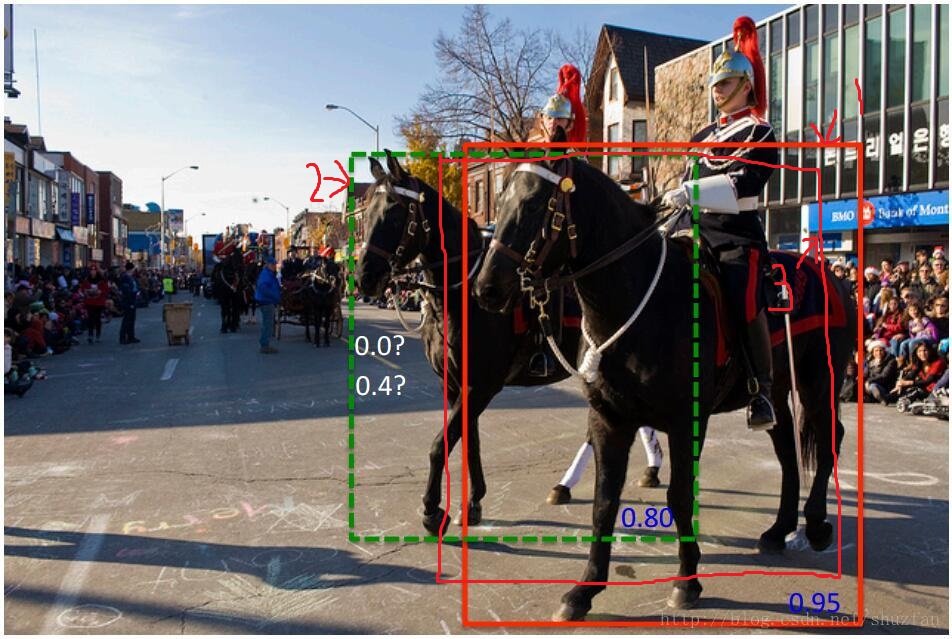
如上图:
假如还检测出了3号框,而我们的最终目标是检测出1号和2号框,并且剔除3号框,原始的nms只会检测出一个1号框并剔除2号框和3号框,而softnms算法可以对1、2、3号检测狂进行置信度排序,可以知道这三个框的置信度从大到小的顺序依次为:1-》2-》3(由于是使用了惩罚,所有可以获得这种大小关系),如果我们再选择了合适的置信度阈值,就可以保留1号和2号,同时剔除3号,实现我们的功能。
但是,这里也有一个问题就是置信度的阈值如何选择,作者在这里依然使用手工设置的值,依然存在很大的局限性,所以该算法依然存在改进的空间。
result:
分类: image processing,machine learning
好文要顶 关注我 收藏该文 


outthinker
关注 - 9
粉丝 - 65
+加关注
0
0
« 上一篇:C++ Boost库简介(转载)
» 下一篇:sublime3添加python编译系统
posted @ 2018-03-09 09:47 outthinker 阅读(1809) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏
