做外贸的怎样才能上国外网站查看浏览过的历史记录百度
文章目录
- 前言:
- 1. 线程概念
- 1.1. 什么是线程
- 1.2. 线程得优点:
- 1.3. 线程的缺点
- 线程异常
- 线程的用途
- 2. 线程的理解(Linux 系统为例)
- 2.1. 为什么要设计Linux“线程"?
- 2.2. 什么是进程?
- 2.3. 关于调度的问题
- 2.4. 再谈地址空间(页表、虚拟地址和物理地址)
- 4. 线程的控制
- 4.1. 线程的创建
- 4.2. 进程等待
- 4.3. 进程终止
- 4.4. 进程分离:
- 5. Linux进程 VS 线程
- 6. 在C++11 也带了多线程
- 总结:
前言:
在现代计算机系统中,多任务处理和并行计算的需求日益增长,这推动了线程技术的发展和应用。线程作为进程的一个执行单元,允许操作系统更高效地进行任务调度和管理。本文旨在深入探讨线程的概念、优势、缺点以及在Linux系统中的具体实现和控制方式。通过分析线程与进程的关系,以及C++11中多线程的支持,本文将为读者提供一个全面的线程技术概览。
1. 线程概念
线程是进程内部的一个执行分支,线程是CPU调度的基本单位
加载到内存中的程序,叫做进程。 修正:进程 = 内核数据结构 + 进程代码和数据
1.1. 什么是线程
- 在一个程序里的一个执行路线就叫做线程(thread)。更准确的定义是:线程是“一个进程内部的控制序列”
- 一切进程至少都有一个执行线程
- 线程在进程内部运行,本质是在进程地址空间内运行
- 在Linux系统中,在CPU眼中,看到的PCB都要比传统的进程更加轻量化
- 透过进程虚拟地址空间,可以看到进程的大部分资源,将进程资源合理分配给每个执行流,就形成了线程执行流
1.2. 线程得优点:
- 创建一个新线程的代价要比创建一个新进程小得多
- 与进程之间的切换相比,线程 之间的切换需要操作系统做的工作要少很多
- 线程占用的资源要比进程少很多
- 能充分利用多处理器的可并行数量
- 在等待慢速I/O操作结束的同时,程序可执行其他的计算任务
- 计算密集型应用,为了能在多处理器系统上运行,将计算分解到多个线程中实现
- I/O密集型应用,为了提高性能,将I/O操作重叠。线程可以同时等待不同的I/O操作。
1.3. 线程的缺点
- 性能损失
一个很少被外部事件阻塞的计算密集型线程往往无法与共它线程共享同一个处理器。如果计算密集型线程的数量比可用的处理器多,那么可能会有较大的性能损失,这里的性能损失指的是增加了额外的同步和调度开销,而可用的资源不变。 - 健壮性降低
编写多线程需要更全面更深入的考虑,在一个多线程程序里,因时间分配上的细微偏差或者因共享了不该共享的变量而造成不良影响的可能性是很大的,换句话说线程之间是缺乏保护的。 - 缺乏访问控制
进程是访问控制的基本粒度,在一个线程中调用某些OS函数会对整个进程造成影响。编程难度提高编写与调试一个多线程程序比单线程程序困难得多
线程异常
- 单个线程如果出现除零,野指针问题导致线程崩溃,进程也会随着崩溃。
- 线程是进程的执行分支,线程出异常,就类似进程出异常,进而触发信号机制,终止进程,进程终止,该进程内的所有线程也就随即退出。
线程的用途
- 合理的使用多线程,能提高CPU密集型程序的执行效率。
- 合理的使用多线程,能提高IO密集型程序的用户体验(如生活中我们一边写代码一边下载开发工具,就是多线程运行的一种表现)
2. 线程的理解(Linux 系统为例)
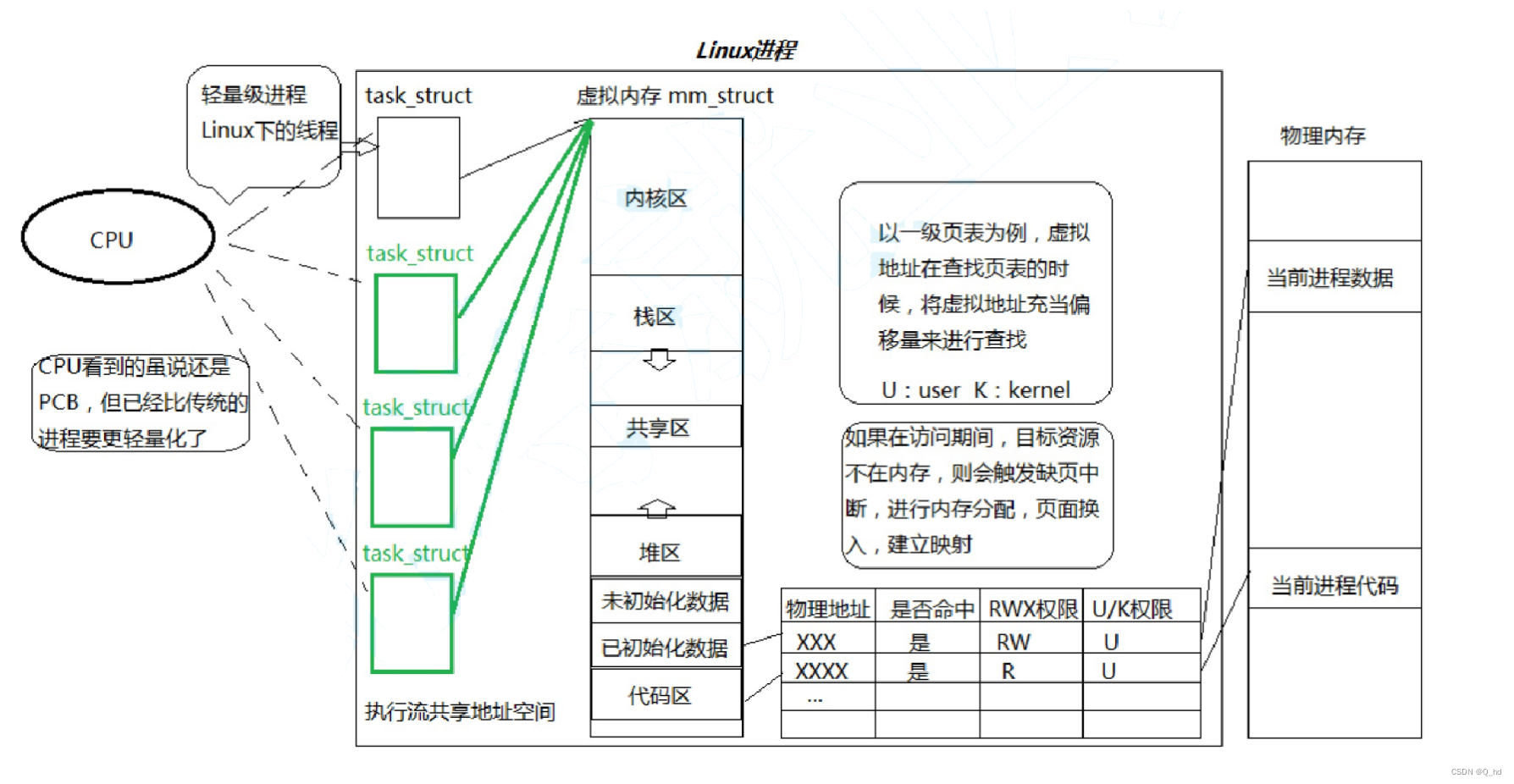
正文:代码段(区),我们的代码在进程中,全部都属串行调用的!
进程创建,成本较高,时间和空间
地址空间和地址空间上的虚拟地址,本质是一种“资源”
2.1. 为什么要设计Linux“线程"?
如果我们要设计线程,OS也要对线程进行管理!先描述,再组织
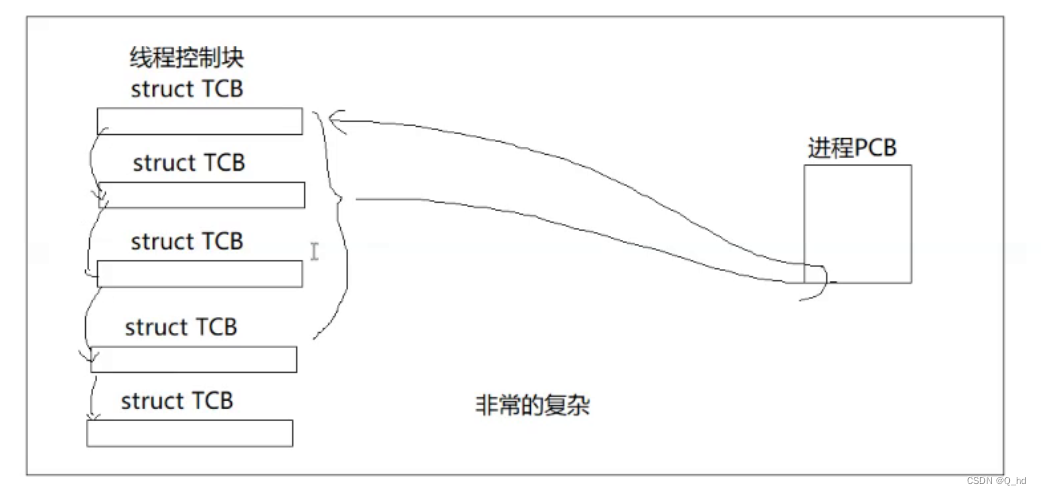
Linux 的设计者认为,进程和线程都是执行流,具有极度的相似性,没有必要单独设计数据结构和算法,直接复用代码,使用进程来模拟线程!
以前的进程:一个内部只有一个线程的进程。
今天的进程:一个内部至少右一个线程的进程。
在现在来看,以前所学的进程,是今天的特殊情况。
2.2. 什么是进程?
进程的内核角度:承担分配系统资源的基本实体(不要站在调度的角度理解进程,而因该站在资源的角度理解进程)
2.3. 关于调度的问题
不用区分task_struct(进程?都是执行流!)
线程<=执行流(轻量级进程)<=进程
Linux中,所有的调度执行流,都叫做:轻量级进程。
2.4. 再谈地址空间(页表、虚拟地址和物理地址)
多个执行流是如何进行代码划分?如何理解?
- 操作系统要不要管理内存呢?
用4KB数据块
用页框或者页帧
struct Page
{int flag;// 其他属性
}
struct page mem[1048579]; // 对内存的管理就是对数组的增删查改!
给不同的线程分配表不同的区域,本质就是给让不同的线程,各自看到全部页表的子集!
4. 线程的控制
4.1. 线程的创建
// testThread.cc
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>void *newThreadRun(void *args)
{while (true){std::cout << "I am new thread,pid: " << getpid() <<std::endl;sleep(1);}
}int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, newThreadRun, nullptr); // 线程创建while (true) {std::cout << "I am main thread,pid: " << getpid() << std::endl;sleep(1);}return 0;
}
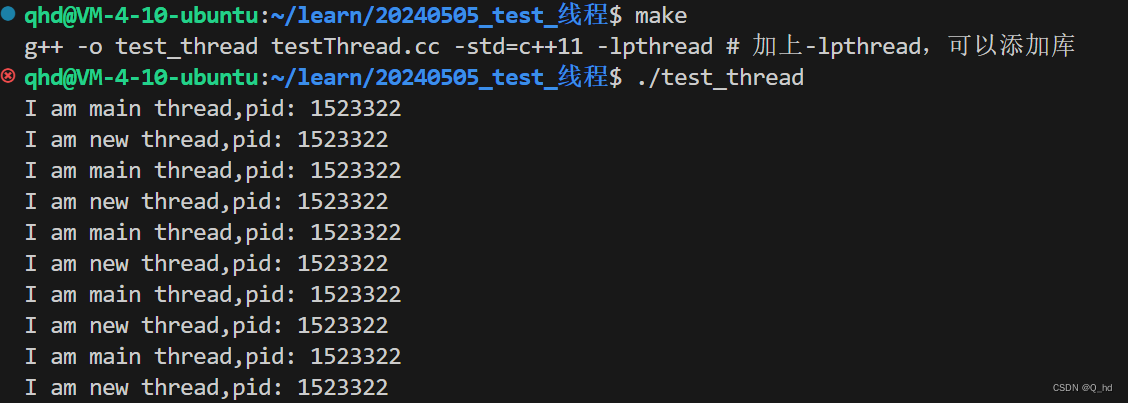
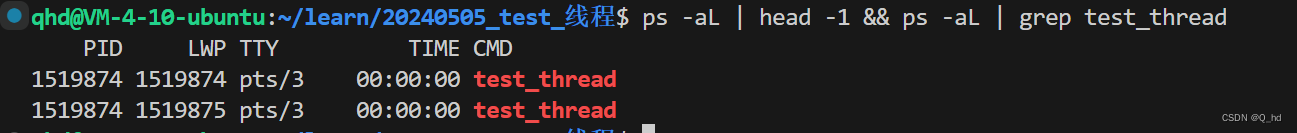
LWP:light weight process: 轻量级进程
所以,操作系统在进行调度的时候,用哪个id来进行调度呢?LWP
单进程,多进程? 每一个进程内部都只有一个执行流,LWP == PID
函数编译完成后,是若干行代码块,函数名是该代码块的入口地址。
最后形成的是一个可执行程序——所有的函数,都按照地址空间统一编址!
用户知道“轻量级进程”这个概念吗? 没有! 进程和线程。
将轻量级进程的系统调用进行封装,转成线程相关的接口语义提供给用户(pthread库——原生线程库,Linux系统自带,但不在内核,用户级线程)
所以Linux有没有真线程呢?没有,Linux 只有轻量级进程。
Linux 系统,不会有线程相关的系统调用,只有轻量级进程的系统调用。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <pthread.h> // 原生线程库的头文件
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>std::string ToHex(pthread_t tid)
{char id[64]; snprintf(id, sizeof(id), "0x%lx", tid);return id;
}void* newThreadRun(void* args)
{std::string threadname = (char*)args;int cnt = 5;while (cnt){std::cout << threadname << " is running " << cnt << ", pid:" << getpid() << ",mythread id:" << ToHex(pthread_self()) << std::endl;sleep(1);--cnt;}return nullptr;
}int main()
{ // 1. idpthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, newThreadRun, (void*)"thread-1");// 2. 新和主两个线程,谁先运行呢?不确定,由调度器决定int cnt = 10;while (cnt) {std::cout << "I am main thread:" << cnt << ",pid: " <<getpid() << ",new thread id:" << ToHex(tid) << ",mainthread id:"<< ToHex(pthread_self()) << std::endl;sleep(1);--cnt;}return 0;
}
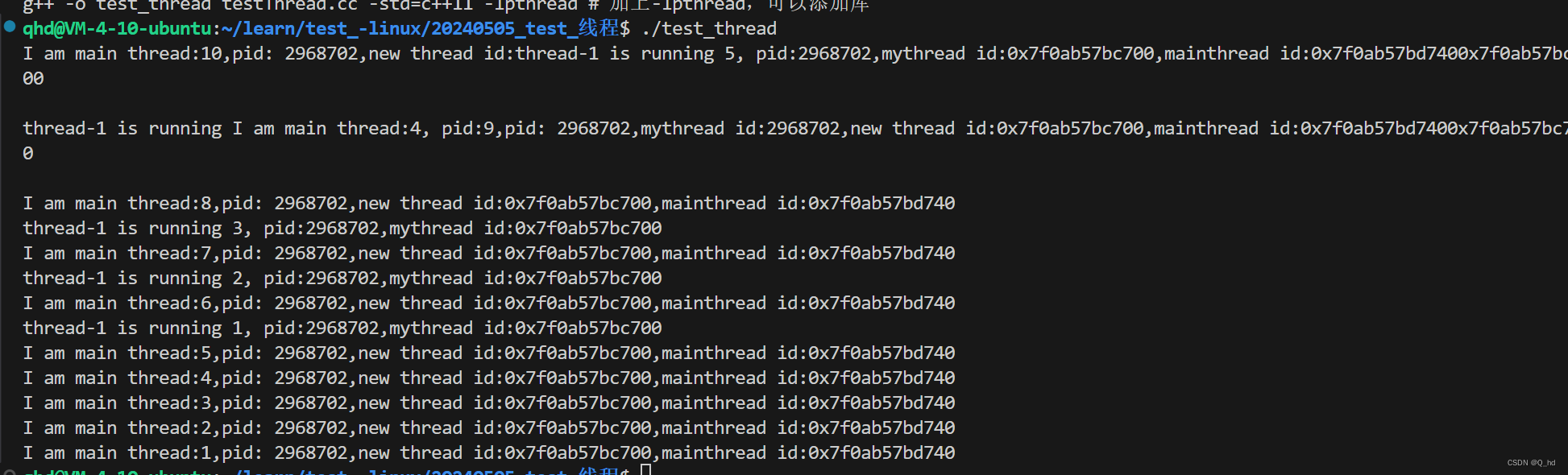
主进程与线程的id,都是可以获取的。
因为新旧进程的执行顺序是不确定的,所以开始两条打印时,会造成混再一起打印。
4.2. 进程等待
int n = pthread_join(tid, nullptr/*输出型参数*/); // 线程等待
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <pthread.h> // 原生线程库的头文件
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>std::string ToHex(pthread_t tid)
{char id[64]; snprintf(id, sizeof(id), "0x%lx", tid);return id;
}void* newThreadRun(void* args)
{std::string threadname = (char*)args;int cnt = 5;while (cnt){std::cout << threadname << " is running " << cnt << ", pid:" << getpid() << ",mythread id:" << ToHex(pthread_self()) << std::endl;sleep(1);--cnt;}return nullptr;
}int main()
{ pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, newThreadRun, (void*)"thread-1");sleep(3);// 主线程退出 == 进程退出 == 所有线程都要退出// 1. 往往我们需要main thread最后结束// 2. 线程也要被“wait”,要不然会产生类似进程那里的内存泄 漏的问题 int n = pthread_join(tid, nullptr); // 线程等待std::cout << "main thread quit, n = " << n << std::endl; sleep(5);return 0;
}
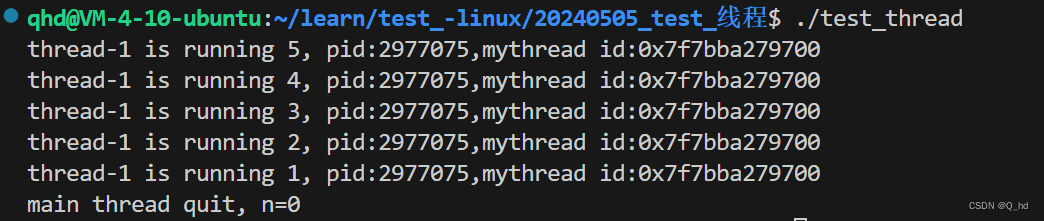
4.3. 进程终止
return
pthread_exit
pathread_cancel
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <pthread.h> // 原生线程库的头文件
#include <unistd.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <sys/types.h>// 同一个进程内的线程,大部分资源都是共享的,地址空间是共享的。
int g_val = 100;std::string ToHex(pthread_t tid)
{ char id[64]; snprintf(id, sizeof(id), "0x%lx", tid);return id;
}// 线程退出// 1. 代码跑完,结果对// 2. 代码跑完,结果不对// 3. 出异常了 —— 重点 —— 多线程中,任何一个线程出现异常(div 0, 野指针),都会导致整个进程退出。—— 多线程代码往往健壮性不好
void* newThreadRun(void* args)
{std::string threadname = (char*)args;int cnt = 5;while (cnt){std::cout << threadname << " is running " << cnt << ", pid:" << getpid() << ",mythread id:" << ToHex(pthread_self()) << ",g_val: "<< g_val << ",&g_val: "<< &g_val << std::endl;++g_val;sleep(1);// int *p = nullptr;// *p == 100; //故意一个野指针--cnt;}// 1. 线程函数结束// 2. pthread_exit((void*)123);//exit(10); // 不能用exit终止线程,因为它是终止进程的。// return (void*)123; // 返回给退出信息,warning}int main()
{ // 1. idpthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, newThreadRun, (void*)"thread-1");// // 在主线程中,你保证新的进程已经启动// sleep(2);// pthread_cancel(tid); // 取消线程, 线程返回退出值-1.sleep(3);// 主线程退出 == 进程退出 == 所有线程都要退出// 1. 往往我们需要main thread最后结束// 2. 线程也要被“wait”,要不然会产生类似进程那里的内存泄 漏的问题 // // 2. 新和主两个线程,谁先运行呢?不确定,由调度器决定// int cnt = 10;// while (cnt) // {// std::cout << "I am main thread:" << cnt << ",pid: " <<getpid() // << ",new thread id:" << ToHex(tid) << ",mainthread id:"<< ToHex(pthread_self()) // << ",g_val: "<< g_val << ",&g_val: "<< &g_val << std::endl;// sleep(1);// --cnt;// }void* ret = nullptr;int n = pthread_join(tid, &ret); //我们怎么没有像进程一样获取线程的退出信号呢?只有你手动写的退出码// 不考虑线程的异常退出情况std::cout << "main thread quit, n = " << n << ",main thread get a ret: " << (long long)ret << std::endl; return 0;
}

与进程之间切换相比,线程之间得切换需要操作系统做的工作要少很多。
4.4. 进程分离:
进程分离通常是指将一个线程的生命周期从其创建者的控制中分离出来,使得线程成为一个独立运行的执行流。在多线程编程中,特别是在使用POSIX线程库(pthread)时,pthread_detach()函数是用来实现线程分离的关键操作。
pthread_detach(tid);
5. Linux进程 VS 线程
- 进程是资源分配的基本单位
- 线程是调度的基本单位
- 线程共享进程数据,但也拥有自己的一部分数据:
- 线程ID
- 一组寄存器
- 栈
- errno
- 信号屏蔽字
- 调度优先级
进程的多个线程共享 同一地址空间,因此Text Segment、Data Segment都是共享的,如果定义一个函数,在各线程中都可以调用,如果定义一个全局变量,在各线程中都可以访问到,除此之外,各线程还共享以下进程资源和环境:
-
文件描述符表
-
每种信号的处理方式(SIG_ IGN、SIG_ DFL或者自定义的信号处理函数)
-
当前工作目录
-
用户id和组id
进程和线程的关系如下图:
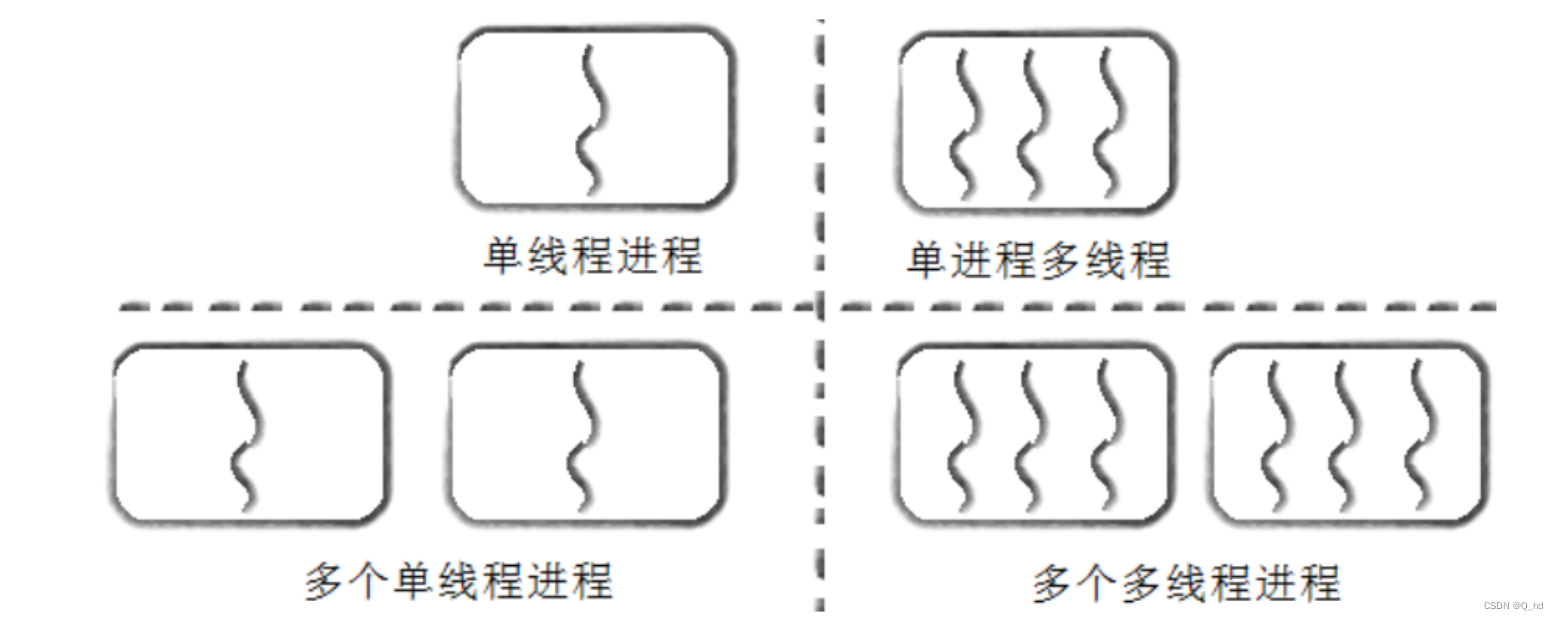
-
线程私有:
- 线程的硬件上下文数据(CPU寄存器的值)(调度)
- 线程的独立栈结构(长规运行)
-
线程共享:
- 代码和全局数据
- 进程文件描述符表
1.一个线程出问题,导致其它线程也出问题,导致整个进程退出——线程安全问题
2.多线程中,公共函数如果被多个线程同时进入——该函数被重入。
6. 在C++11 也带了多线程
#include <iostream>
#include <thread> // C++
#include <vector>
#include <unistd.h>void threadrun(int num)
{while (num){std::cout << "I am a thread num: " << num << std::endl;sleep(1);}
}int main()
{ std::vector<std::thread> threads;int num_threads = 5;int thread_count = 10;for (int i = 0; i < num_threads; ++i) {threads.push_back(std::thread(threadrun, thread_count));}while (true){std::cout << "I am a main thread" << std::endl;sleep(1);}for (auto& t : threads) {t.join(); // 等待线程结束}return 0;
}
C++ 中的多线程,是对原生线程的封装。
1.为什么要做封装? 通过C++标准库,增加语言的跨平台
2.windows呢? 和Linux库不一样,不需要包含pthread库
3.其他语言呢? Linux提供多线程的底层的唯一方式
理解pthread:系统中没有线程,只有轻量级进程的概念
用户能不能通过接口,管理线程呢?比如创建,终止等待等。
线程的封装示例:
#ifndef __THREAD_HPP__
#define __THREAD_HPP__#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <functional>
#include <pthread.h>namespace ThreadModule
{template<typename T>using func_t = std::function<void(T&)>;// typedef std::function<void(const T&)> func_t;template<typename T>class Thread{public:void Excute(){_func(_data);}public:Thread(func_t<T> func, T &data, const std::string &name="none-name"): _func(func), _data(data), _threadname(name), _stop(true){}static void *threadroutine(void *args) // 类成员函数,形参是有this指针的!!{Thread<T> *self = static_cast<Thread<T> *>(args);self->Excute();return nullptr;}bool Start(){int n = pthread_create(&_tid, nullptr, threadroutine, this);if(!n){_stop = false;return true;}else{return false;}}void Detach(){if(!_stop){pthread_detach(_tid);}}void Join(){if(!_stop){pthread_join(_tid, nullptr);}}std::string name(){return _threadname;}void Stop(){_stop = true;}~Thread() {}private:pthread_t _tid;std::string _threadname;T &_data; // 为了让所有的线程访问同一个全局变量func_t<T> _func;bool _stop;};
} // namespace ThreadModule#endif
总结:
本文全面介绍了线程的基础知识和在Linux系统中的应用。首先,我们定义了线程,并讨论了线程相比进程的优势,如资源占用少、创建和切换成本低,以及能够提高多处理器系统的并行计算能力。同时,也指出了线程的缺点,包括潜在的性能损失、健壮性降低和缺乏访问控制,这些缺点要求开发者在编写多线程程序时需要更加谨慎和深入的理解。
接着,文章以Linux系统为例,解释了线程的设计哲学,即利用进程的概念来模拟线程,这样做的好处是复用了现有的进程管理机制,减少了系统设计的复杂性。同时,我们也讨论了线程在内存管理、调度和控制方面的细节,包括线程的创建、等待、终止和分离等操作。
此外,本文还对比了Linux进程与线程的区别,指出了线程共享和私有的数据,以及线程安全和重入性问题。最后,文章介绍了C++11标准库对多线程的支持,展示了如何使用C++11的库来创建和管理线程,并提供了一个简单的线程封装示例,说明了C++多线程是对原生线程的高级封装,增强了跨平台的特性。
