网站优化建设郑州兰州seo网站建设
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、AVL 树介绍
- 二、AVL树节点的定义
- 三、AVL树的插入
- 四、AVL树的旋转
- 五、AVL树的验证
- 六、AVL树的删除
- 七、AVL树的性能
- 八、AVL树的实现
前言
在前面的文章中介绍了map / multimap / set / multiset 容器,这几个容器的底层都是按照二叉搜索树来实现的。但是二叉搜索树有其自身的缺陷,假如往树中插入的元素有序或者接近有序,二叉搜索树就会退化成单支树,时间复杂度会退化成O(N)。因此 map、set 等关联式容器的底层结构是对二叉树进行了平衡处理,即采用平衡树来实现。
一、AVL 树介绍
二叉搜索树虽可以缩短查找的效率,但如果数据有序或接近有序二叉搜索树将退化为单支树,查找元素相当于在顺序表中搜索元素,效率低下。因此,两位俄罗斯的数学家G.M.Adelson-Velskii和E.M.Landis在1962年发明了一种解决上述问题的方法:当向二叉搜索树中插入新结点后,如果能保证每个结点的左右子树高度之差的绝对值不超过1(需要对树中的结点进行调整),即可降低树的高度,从而减少平均搜索长度。
AVL树是一棵二叉搜索树,且高度平衡,因此AVL树也叫高度平衡二叉搜索树。如果AVL树有n个结点,其 高度可保持在O(log2N)O(log_2 N)O(log2N),搜索时间复杂度O(log2N)O(log_2 N)O(log2N)。
AVL树的性质
- 任意一颗子树的左右子树都是AVL树
- 任意一颗子树的左右子树高度之差(简称平衡因子)的绝对值不超过1
二、AVL树节点的定义
template<class K, class V>
struct AVLTreeNode
{AVLTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _kv(kv), _bf(0){}AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _left; // 该节点的左孩子AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _right; // 该节点的右孩子AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _parent; // 该节点的双亲pair<K, V> _kv;int _bf; // 该节点的平衡因子
};
三、AVL树的插入
AVL树的插入过程可以分为两步:
- 先按照二叉搜索树的规则将节点插入到AVL树中
- 新节点插入后,AVL树的平衡性可能会遭到破坏,此时就需要更新平衡因子,并检测是否破坏了AVL树的平衡性。
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(kv);return true;}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;// 找插入节点的位置while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return false;}}// 插入节点cur = new Node(kv);// 链接cur和parentif (parent->_kv.first < kv.first){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;// 控制平衡while (parent) //最坏的情况是更新到根才会停止{// 更新平衡因子。新增在右,parent的平衡因子++ ;新增在左,parent的平衡因子--if (cur == parent->_right)parent->_bf++;elseparent->_bf--;if (parent->_bf == 0)//更新后,parent的平衡因子为0,说明插入后两边一样高,插入填入了矮的部分,parent所在子树高度不变,不需要继续往上更新。{break;}else if (abs(parent->_bf) == 1)//更新后,abs(parent的平衡因子)为1,说明插入后有一边高,parent所在子树高度变了,需要继续往上更新。{parent = parent->_parent;cur = cur->_parent;}else if (abs(parent->_bf) == 2)//更新后,abs(parent的平衡因子)为2,说明已经打破平衡,parent所在子树需要旋转处理。{if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == 1){RotateL(parent);}else if ((parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == -1)){RotateR(parent);}else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == 1){RotateLR(parent);}else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == -1){RotateRL(parent);}else{assert(false);}break; //一次插入只会有一次旋转,旋转完成了直接break}else //更新后,abs(parent的平衡因子)大于2,说明插入前就不是AVL树,需要检查之前的操作{assert(false);}}return true;
}
四、AVL树的旋转
旋转原则:1. 旋转为平衡树 2. 保持搜索树规则
新节点插入较高右子树的右侧—右右:左单旋

// 新节点插入较高右子树的右侧---右右:左单旋
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL) //subRL可能为空subRL->_parent = parent;Node* ppNode = parent->_parent; //注意:有可能parent不是根节点,保存上一层节点subR->_left = parent;parent->_parent = subR;if (_root == parent) //parent是整棵树的根{_root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}else //parent是子树的根{if (ppNode->_left == parent)//判断上一层节点和parent的关系{ppNode->_left = subR;}else{ppNode->_right = subR;}subR->_parent = ppNode;}subR->_bf = parent->_bf = 0; //修改平衡因子
}
新节点插入较高左子树的左侧—左左:右单旋
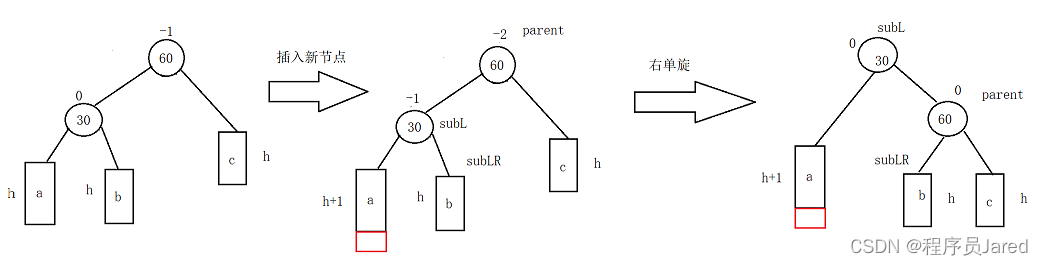
// 新节点插入较高左子树的左侧---左左:右单旋
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_parent = parent;Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;subL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (_root == parent){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (ppNode->_left == parent){ppNode->_left = subL;}else{ppNode->_right = subL;}subL->_parent = ppNode;}subL->_bf = parent->_bf = 0;
}
新节点插入较高左子树的右侧—左右:先左单旋再右单旋
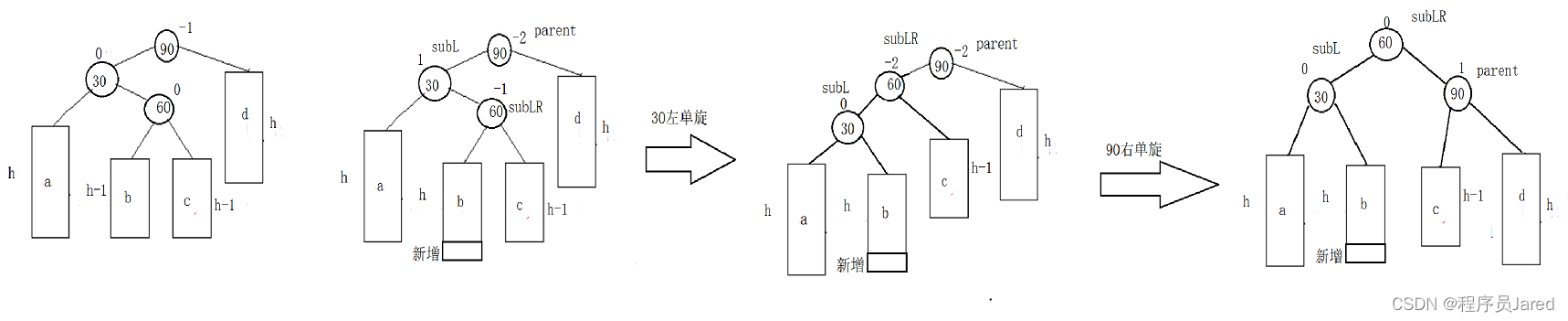
在b或者c的位置插入,都会引起bf的变化,引发双旋。将双旋变成单旋后再旋转,即:先对30进行左单旋,然后再对90进行右单旋,旋转完成后再考虑平衡因子的更新。
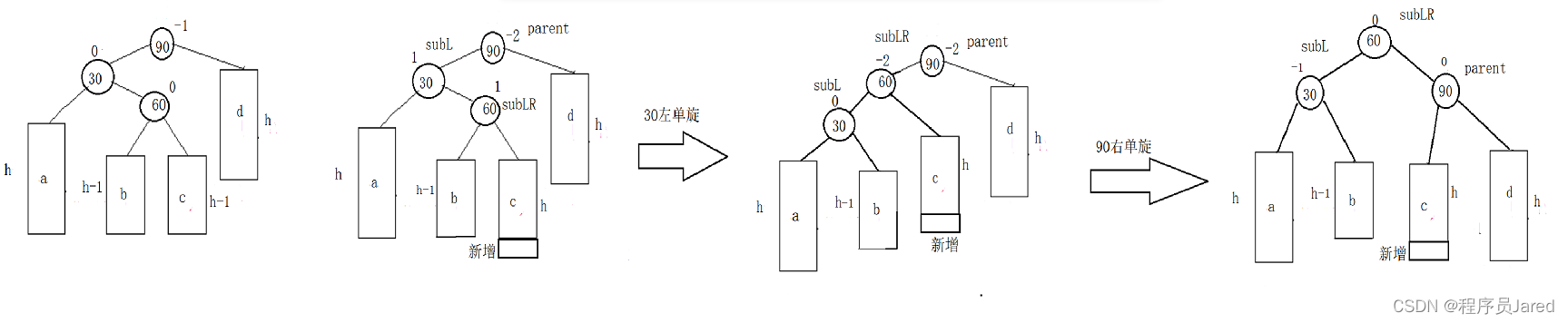
// 新节点插入较高左子树的右侧---左右:先左单旋再右单旋
void RotateLR(Node* parent)
{Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;int bf = subLR->_bf; //记录subLR的平衡因子,根据它的大小将其他平衡因子的更新分为三种情况RotateL(parent->_left); // 先cur左旋再parent右旋RotateR(parent);subLR->_bf = 0;if (bf == 1) // c插入{parent->_bf = 0;subL->_bf = -1;}else if (bf == -1) // b插入{parent->_bf = 1;subL->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 0) //a,b,c,d为空树,subLR为新增{parent->_bf = 0;subL->_bf = 0;}else // 说明出问题了{assert(false);}
}
新节点插入较高右子树的左侧—右左:先右单旋再左单旋
整体思路同上:
//新节点插入较高右子树的左侧——右左:先右单旋再左单旋
void RotateRL(Node* parent)
{Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;int bf = subRL->_bf;RotateR(parent->_right);RotateL(parent);subRL->_bf = 0;if (bf == 1){subR->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = -1;}else if (bf == -1){subR->_bf = 1;parent->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 0){parent->_bf = 0;subR->_bf = 0;}else{assert(false);}
}
总结
假如以Parent为根的子树不平衡,即Parent的平衡因子为2或者-2,分以下情况考虑:
- Parent的平衡因子为2,说明Parent的右子树高,设Parent的右子树的根为SubR。当SubR的平衡因子为1时,执行左单旋。当SubR的平衡因子为-1时,执行右左双旋。
- Parent的平衡因子为-2,说明Parent的左子树高,设Parent的左子树的根为SubL。当SubL的平衡因子为-1是,执行右单旋。当SubL的平衡因子为1时,执行左右双旋。
旋转完成后,原Parent为根的子树个高度降低,已经平衡,不需要再向上更新。
旋转的意义
- 平衡
- 降高度
五、AVL树的验证
验证其为二叉搜索树
如果中序遍历可得到一个有序的序列,就说明为二叉搜索树
public:void InOrder(){_InOrder(_root);cout << endl;}private:void _InOrder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}_InOrder(root->_left);cout << root->_kv.first << ":" << root->_kv.second << endl;_InOrder(root->_right);}
验证其为平衡树
每个节点子树高度差的绝对值不超过1,节点的平衡因子是否计算正确
public:bool IsBalance(){return _IsBalance(_root);}private:int Height(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return 0;return max(Height(root->_left), Height(root->_right)) + 1;} bool _IsBalance(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return true;}int leftHT = Height(root->_left);int rightHT = Height(root->_right);int diff = rightHT - leftHT;if (diff != root->_bf){cout << root->_kv.first << "平衡因子异常" << endl;return false;}return abs(diff) < 2&& _IsBalance(root->_left)&& _IsBalance(root->_right);}
六、AVL树的删除
因为AVL树也是二叉搜索树,可按照二叉搜索树的方式将节点删除,然后再更新平衡因子,只不错与删除不同的时,删除节点后的平衡因子更新,最差情况下一直要调整到根节点的位置。
七、AVL树的性能
AVL树是一棵绝对平衡的二叉搜索树,其要求每个节点的左右子树高度差的绝对值都不超过1,这样可以保证查询时高效的时间复杂度为O(log2N)O(log_2 N)O(log2N)。
但是如果要对AVL树做一些结构修改的操作,性能非常低下,比如:插入时要维护其绝对平衡,旋转的次数比较多,更差的是在删除时,有可能一直要让旋转持续到根的位置。
因此:如果需要一种查询高效且有序的数据结构,而且数据的个数为静态的,可以考虑AVL树,但一个结构经常修改,就不太适合。
八、AVL树的实现
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include<time.h>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;template<class K, class V>
struct AVLTreeNode
{AVLTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _kv(kv), _bf(0){}AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _left; // 该节点的左孩子AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _right; // 该节点的右孩子AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _parent; // 该节点的双亲pair<K, V> _kv;int _bf; // 该节点的平衡因子
};template<class K, class V>
struct AVLTree
{typedef AVLTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(kv);return true;}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;// 找插入节点的位置while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return false;}}// 插入节点cur = new Node(kv);// 链接cur和parentif (parent->_kv.first < kv.first){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;// 控制平衡while (parent) //最坏的情况是更新到根才会停止{// 更新平衡因子。新增在右,parent的平衡因子++ ;新增在左,parent的平衡因子--if (cur == parent->_right)parent->_bf++;elseparent->_bf--;if (parent->_bf == 0)//更新后,parent的平衡因子为0,说明插入后两边一样高,插入填入了矮的部分,parent所在子树高度不变,不需要继续往上更新。{break;}else if (abs(parent->_bf) == 1)//更新后,abs(parent的平衡因子)为1,说明插入后有一边高,parent所在子树高度变了,需要继续往上更新。{parent = parent->_parent;cur = cur->_parent;}else if (abs(parent->_bf) == 2)//更新后,abs(parent的平衡因子)为2,说明已经打破平衡,parent所在子树需要旋转处理。{if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == 1){RotateL(parent);}else if ((parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == -1)){RotateR(parent);}else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == 1){RotateLR(parent);}else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == -1){RotateRL(parent);}else{assert(false);}break; //一次插入只会有一次旋转,旋转完成了直接break}else //更新后,abs(parent的平衡因子)大于2,说明插入前就不是AVL树,需要检查之前的操作{assert(false);}}return true;}void InOrder(){_InOrder(_root);cout << endl;}bool IsBalance(){return _IsBalance(_root);}
private:bool _IsBalance(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return true;}int leftHT = Height(root->_left);int rightHT = Height(root->_right);int diff = rightHT - leftHT;if (diff != root->_bf){cout << root->_kv.first << "平衡因子异常" << endl;return false;}return abs(diff) < 2&& _IsBalance(root->_left)&& _IsBalance(root->_right);}int Height(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return 0;return max(Height(root->_left), Height(root->_right)) + 1;}// 新节点插入较高右子树的右侧---右右:左单旋void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL) //subRL可能为空subRL->_parent = parent;Node* ppNode = parent->_parent; //注意:有可能parent不是根节点,保存上一层节点subR->_left = parent;parent->_parent = subR;if (_root == parent) //parent是整棵树的根{_root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}else //parent是子树的根{if (ppNode->_left == parent)//判断上一层节点和parent的关系{ppNode->_left = subR;}else{ppNode->_right = subR;}subR->_parent = ppNode;}subR->_bf = parent->_bf = 0; //修改平衡因子}// 新节点插入较高左子树的左侧---左左:右单旋void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_parent = parent;Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;subL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (_root == parent){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (ppNode->_left == parent){ppNode->_left = subL;}else{ppNode->_right = subL;}subL->_parent = ppNode;}subL->_bf = parent->_bf = 0;}// 新节点插入较高左子树的右侧---左右:先左单旋再右单旋void RotateLR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;int bf = subLR->_bf; //记录subLR的平衡因子,根据它的大小将其他平衡因子的更新分为三种情况RotateL(parent->_left); // 先cur左旋再parent右旋RotateR(parent);subLR->_bf = 0;if (bf == 1) // c插入{parent->_bf = 0;subL->_bf = -1;}else if (bf == -1) // b插入{parent->_bf = 1;subL->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 0) //a,b,c,d为空树,subLR为新增{parent->_bf = 0;subL->_bf = 0;}else // 说明出问题了{assert(false);}}//新节点插入较高右子树的左侧——右左:先右单旋再左单旋void RotateRL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;int bf = subRL->_bf;RotateR(parent->_right);RotateL(parent);subRL->_bf = 0;if (bf == 1){subR->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = -1;}else if (bf == -1){subR->_bf = 1;parent->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 0){parent->_bf = 0;subR->_bf = 0;}else{assert(false);}}void _InOrder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}_InOrder(root->_left);cout << root->_kv.first << ":" << root->_kv.second << endl;_InOrder(root->_right);}
private:Node* _root = nullptr;
};void TestAVLTree1()
{int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14 }; // 测试双旋平衡因子调节//int a[] = { 16, 3, 7, 11, 9, 26, 18, 14, 15 };AVLTree<int, int> t1;for (auto e : a){t1.Insert(make_pair(e, e));}t1.InOrder();cout << "IsBalance:" << t1.IsBalance() << endl;
}void TestAVLTree2()
{size_t N = 10000;srand(time(0));AVLTree<int, int> t1;for (size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i){int x = rand();t1.Insert(make_pair(x, i));}cout << "IsBalance:" << t1.IsBalance() << endl;
}
